Tuvalu, an island nation in the South Pacific is located. This small nation of islands was once home to Polynesians. During the 14th and 17th centuries, the islands were populated by migrants from other parts of the South Pacific. Tuvaluans were a scattered people, and their population was about 3,000 at the time of European contact. Most of the inhabitants were descendants of migrants.
Europeans first explored the region in the 18th century. Clvaro de Mendaa de Neyra, a Spanish navigator, made the first European trip to Tuvalu. Europeans began to forcefully recruit plantation workers to the islands after the discovery. Many of the inhabitants were kidnapped and forced to work in plantations. Others emigrated to larger Gilbert Islands.

Tuvalu was British protectorate up until 1978 when it became an independent country. Today, Tuvaluans comprise the majority of the population. A significant number of residents are also of other Pacific ethnicities. People of other Pacific ethnicities often marry Tuvaluans.
Tuvalu's principal economic priority, according to the government, is to develop its economy without any foreign assistance. Nearly 20 percent of workers are employed by the government. Tuvalu is a small country with a very stable economy. However, it has never suffered strikes or economic crises.
Tuvalu is a member UPU, UN and ACP Group. It is also a member of UNESCO, IMO, FAO, UNIDO, and the Asian Development Bank. The government actively participates in global efforts against global warming and pollution. The Tuvalu government has been urging industrialized countries to ratify the Kyoto Protocol.
Tuvalu's economy consists of fishing, agriculture and subsistence farming. Copra is the main cash crop. A lack of arable land means that there is little arable land. However, farmers are able to sell some of their produce, and some manufacture is available for export. About 25 percent of GDP is made up by agricultural products.

Since 1986, Tuvalu's government has made a series of reforms. The population has risen. The United Nations reports that Tuvalu's population was 10,000 in 2005. This number is expected increase to about 14,000 by 2025. Around 6,000 Tuvaluans over 65 are considered to be elderly.
The government of Tuvalu has not imposed any official political parties. Instead, 12 members make up the local parliament, which is generally organized into factions. The Tuvaluan constitution however allows for separation between the church and the state, contrary to other Polynesian countries. Religious organizations also need to register with the government.
Tuvalu Amateur Sports, Boy Scouts, Girl Guides are just three of the most popular organizations in Tuvalu. Other organized youth groups include the Pathfinders and the Tuvalu Youth Fellowship. Students who have completed secondary school can apply to tertiary schools abroad.
The Tuvaluan government doesn't censor or silence media but there are restrictions on speech. Although the media is protected under law, there are no commercial newspapers or television networks. Tuvalu Broadcasting Service transmits local news to Tuvaluan. Access to the Internet is also possible through the Office of the Premier Minister and the Department of Telecommunications.
FAQ
What is the current climate like? How is it changing?
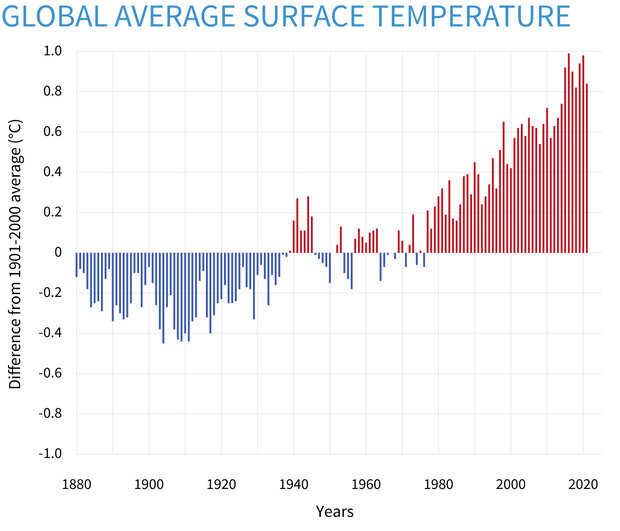
The current climate is characterized by unprecedented uncertainty and change. Temperatures are rising rapidly due to unprecedented levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide. This is causing heat waves, droughts, changes in rainfall patterns, melting of polar ice caps and ocean acidification as well as an increase in sea level.
These changes are already having a profound affect on ecosystems worldwide, causing extinctions or disruptions of habitats. They are also threatening lives and livelihoods for billions of people, especially those who live in areas with resource scarcity.
Increased average surface temperatures, which are caused by human activity, have led to an increase of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or cyclones. This trend will continue as temperatures continue rising.
Global climate change can have a wide range of effects, including rising food security and displacement caused by extreme weather or sea-level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also causing social inequalities, bydisproportionately affecting marginalized groups that lack the knowledge or resources to adapt effectively.
There has been progress in some areas, such as the reduction of carbon emissions or initiatives for renewable energy in certain countries. However, there is no global initiative that can be taken to effectively mitigate these changes. All nations must unite to prevent further destruction and devastation by climate change.
What impact does climate change have on biodiversity and ecosystems
Climate change can have a variety of impacts on biodiversity, ecosystems, and the environment. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
Changes to climate conditions can have drastic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning ecosystems. The hydrological cycle changes can have an impact on the availability of water for aquatic species.
Climate change is also causing rising temperatures and more extremes like droughts/floods. This adds to the stress already placed on fragile systems such coral reefs and tropical rainforests. The climate change will lead to the extermination or decline of as many as 30% of animal species in 2050. This could cause further destruction of ecological communities.
Climate change is therefore a considerable threat not only to biodiversity but also to human societies that depend on functioning ecosystems for food, fresh water, timber, and other services. The best way to minimize its impact is to work at every level to reduce global warming trends. Future damages can be avoided with prudent management practices.
What is the status of international efforts to tackle climate change?
The international effort to tackle climate change has reached a new level of unity and momentum. Countries from all over the globe are increasingly coming together to find ways to reduce their emissions, increase resilience against impacts and invest in renewable energy.
The Paris Agreement has energized collective action at the global level and is a framework that allows individual countries to set voluntary emissions reduction targets. The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, (UNFCCC), provides political guidance and pilots new initiatives like carbon market mechanisms.
In certain regions, there is progress as well. The European Green Deal, for instance, is a comprehensive set of legislation that aims to rebuild Europe's economy while African countries have committed to the African Renewable Energy Initiative. This Initiative aims to increase Africa’s global share of renewable energy production.
Action can also be seen across industries and sectors. Cities are moving towards sustainable public transport, while the whole society is adopting more sustainable lifestyles. Companies are developing technologies to reduce emissions, while investors shift their capital away fossil fuels in favor of renewables.
The OECD committee represents wealthy countries and has established common standards for reporting national climate action through the Common Reporting Framework, also called the 2021 Guidelines.
These efforts demonstrate the importance of climate action. For any chance of reaching the climate goals set forth by science and international law, government, civil society, & private sector actors must build upon this momentum.
What is climate change and how does it occur?
Climate change is the long term shift in global weather patterns resulting from an increase of greenhouse gases. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which causes global temperatures rise. This leads to many changes in weather and climate. These can include rising sea level, melting glaciers or droughts, widespread coral bleaching, species extinction and disruptions in food production.
Human activity is the major cause of climate change. When these activities release massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere it warms the planet at a much faster rate than natural processes like volcanic eruptions as these activities produce many times more emissions than volcanoes.
The deforestation plays an important role in contributing approximately 15-20% to global greenhouse gas emissions. Trees are destroyed or burned to release their carbon dioxide. Forests are also a natural carbon-sink that removes carbon dioxide from the air. Without this absorption capacity, carbon levels will continue increasing with devastating consequences for the ecosystems around the globe.
Human-caused pollution not only releases CO2, but also other harmful gases like methane (CH4) or nitrous oxides (N2O). Methane has been extensively used in industrial processes and contributes greatly to atmospheric warming. Meanwhile, N2O is emitted most commonly from agricultural soil management activities. For example, fertilization or tilling can release excess nitrogen into soil which results in N2O production upon contact with microbial organisms.
To reduce climate change, humanity must unite efforts across the political, social, and economic systems to reduce emissions dramatically and move away from our dependency on fossil fuels toward renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power or low-carbon hydrocarbon fuels. Smart solutions that encourage zero-waste living and replace polluting fossil fuels could help reduce atmospheric pollution and heat buildup. Our environmental impacts can be reduced by adopting preservation measures like reforestation. These projects help to preserve biodiversity and absorb large amounts CO2 from the environment. This helps in addressing climate change and restoring balance for future generation.
What is the climate impact of land use and deforestation?
The climate is directly affected when land use and deforestation are both occurring. If trees are cut down, or burned, carbon dioxide, one the most important greenhouse gases, is no longer absorbed. Therefore, when trees are cleared by deforestation or burned for agricultural purposes, less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere.
Changes in land usage can also cause more greenhouse gasses to be released into the atmosphere. To illustrate, if forests are replaced with agricultural lands to support livestock production, fertilizer and pesticide use could increase methane emissions. Clearance can increase exposure of soils that have large amounts stored carbon. These soils release carbon dioxide when they are turned over or disturbed through farming activities.
Deforestation, land-use change and other environmental impacts can cause more greenhouse gas emissions than they do. It can also affect regional air quality. Smoke from deforestation-related burning events has been shown to cause decreased visibility and health problems such as asthma, as well as other respiratory conditions. Because of the reduced amount of aerosol particles in our atmosphere, which scatter sunlight off the Earth's surface, these changes can have a cumulative impact on global climate.
In conclusion, both deforestation (and land-use) change have been a major contributor to rising levels of global greenhouse gases emissions. Additionally, they have had negative effects on local airquality that has contributed further to climate changes. If serious efforts towards mitigating climate changes are to be made quickly, then reducing these practices must be a priority.
How can the world make a transition to a more sustainable future given the challenges presented by climate change?
Sustainability is the ability for future generations to meet their current needs without compromising their ability to do the same. We must take urgent action to reduce our dependency on finite resources and adopt a more sustainable way of using them.
It is crucial that we reexamine our consumption and production patterns, as well our dependence on fossil fuels, in order to move towards a sustainable future. We must look for new technologies and renewable sources of power, as well as systems that lower harmful emissions and still provide our daily needs.
Furthermore, it is crucial to take a holistic approach to sustainability. This includes all aspects of production including materials, waste management and reuse strategies as well as energy usage in transport and industry. There are many solutions that can be found, such as the utilization of renewable energy, like solar, winds, and hydropower, better waste management, higher efficiency in agriculture, improved transportation networks, green building regulations and sustainable urban planning.
This goal requires behavioral changes from individuals in all sectors of society. Education programs are required to educate people about climate change and show them how they can help create a more sustainable future.
Ultimately, only through collaboration between governments, industry leaders, and citizens will we be able to make significant progress in creating a more sustainable world for generations to come.
How can developing countries and communities cope with the effects of climate changes?
Due to their lack of access to resources, health care systems, and technology, communities and countries in developing countries are more vulnerable to climate change. Climate change can increase the pressure on already limited resources. Floods and droughts can also cause damage to already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can lead to a decrease in crop yields, which will disproportionately affect poorer communities struggling with food insecurity. Extreme weather events like heatwaves or hurricanes can lead to destruction of infrastructure, displacement of people and further perpetuating economic inequality.
The long-term impacts of climate change include resource scarcity, poverty, increased health risks, and an increase of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever. Additionally, flooding will become more common due to rising sea levels and extreme weather. These risks can put lives at high risk in coastal areas with a dearth of infrastructure or emergency services. Not only does it require reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but other measures like better management and access to medical facilities. This will help with the prevention of diseases like Malaria.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Make Your Home More Energy-Efficient and Combat Climate Change
Making your home energy-efficient is one of the best ways to reduce your carbon footprint, save money on utility bills, and make life more comfortable.
Your home should be properly sealed and insulated. You should ensure windows and doors are correctly installed, check for drafts around pipes, vents, and add weather stripping where needed.
To maximize energy efficiency, insulate your ceilings, walls, and floors. Make sure to inspect the attic and any other areas in your home for air leaks.
Lighting can account for as much as 18% of household electricity consumption. Make sure to switch to LED bulbs, which consume up to 80% less electricity compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Additional money can be saved by installing motion sensors, timers, and turning off lights only when needed.
Replacing an old boiler or furnace can dramatically reduce energy bills as newer models are much more efficient. Get a programmable thermostat to adjust the temperature depending on whether people are at home or not.
Switch out all old windows with new double-glazed ones which provide better insulation and don't allow heat to escape through them. Low-flow showerheads are a great option, as they reduce water consumption but maintain adequate pressure.
ENERGY STAR rated items can be used to replace appliances that consume up to 50% less power than noncertified models. Make sure to take care of the little details, such as unplugging TV boxes and phone chargers when not in use. This could help save you significant energy.
These simple steps can reduce your impact on the climate and help you live more efficiently at home.