Carbon dioxide levels have fluctuated between 180 to 300 parts per million over the past 800,000. This current level is unprecedented and is likely to increase. But this is only one difference. There are many things that can influence climate.
According to a recent study carbon dioxide levels 10 times lower in the past than they were today. In fact, they may have been about 50 million years ago. The CO2 levels were comparable to today's and the climate was much more warm back then.
It is clear that carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. But it is important that we also consider temperature. Over a century of research has allowed scientists to examine the Earth's atmosphere. The composition of the atmosphere has been established over the past 800,000. However, the relationship between CO2 and temperature is not yet fully understood. This team of scientists has created a new chemical procedure that can be used as a method to determine CO2 levels in the distant future.
The technique involves determining the ratio of boron to calcium in the shells of ancient single-celled marine algae. Tripati's research team has found the amount of carbon dioxide that was present in the atmosphere over the past 1000 years by taking the average of the rates of calcium & boron over the same period. At the time, the carbon dioxide level was about 280 parts per million.
Tripati's crew is pushing back the record further over the next 20,000,000 year. They are confident that they will be able make accurate estimates for carbon dioxide levels throughout the entire period. If the method succeeds, then we will finally be able to understand the role of carbon dioxide in global warming.
The data can then be integrated with Earth-system models to obtain the most complete understanding of the exchange of carbon dioxide within the atmosphere. Data assimilation uses model simulations in conjunction with actual measurements to get the most realistic picture of the exchange of carbon dioxide through the atmosphere.
OCO-2 satellite (launched in 2014) is designed to measure atmospheric Carbon dioxide at regional scales. Ground-based sensors have previously been used to track measurements. These methods have been widely employed for decades to track CO2 levels rising.
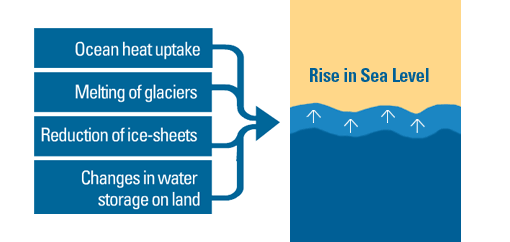
As the Earth warms, CO2 levels should increase. The average atmospheric carbon ppm will reach 600 parts per Million by the 21stcentury. Over the same time, the oceans will heat by 0.2C per decade. Because it absorbs more heat from the earth than the land, oceans are a significant contributor to global warming.
The US Energy Information Administration however reported that fossil-fuel consumption has decreased by nearly 47% within the western nations over the past twenty years. Although this is a very small number, it is an indication of the future.
While the global temperature is not rising over the past decade however, the levels of carbon dioxide have been rapidly increasing. We will continue to see an increase in carbon dioxide levels unless we take action to reduce CO2 emissions.
FAQ
What is the climate change's impact on ecosystems and biodiversity?
Climate change can have many impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changing extreme weather events and sea level, as well as an increase in acidity in oceans, are all issues that affect wildlife and ecosystems.
Changes to climate conditions can have drastic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning ecosystems. Changes in the hydrological cycle can also affect water availability for aquatic species.
Climate changes can lead to higher temperatures and more frequent extremes (such as droughts) which put more stress on already fragile systems, like coral reefs or tropical forests. It is estimated that up to 30% of animal species could become extinct due to climate change by 2050, which would spark a cascade of further losses within ecological communities.
Climate change is therefore a considerable threat not only to biodiversity but also to human societies that depend on functioning ecosystems for food, fresh water, timber, and other services. At all levels, efforts should be made to decrease global warming trends. Future damage should be avoided if possible through careful management.
What causes climate change?
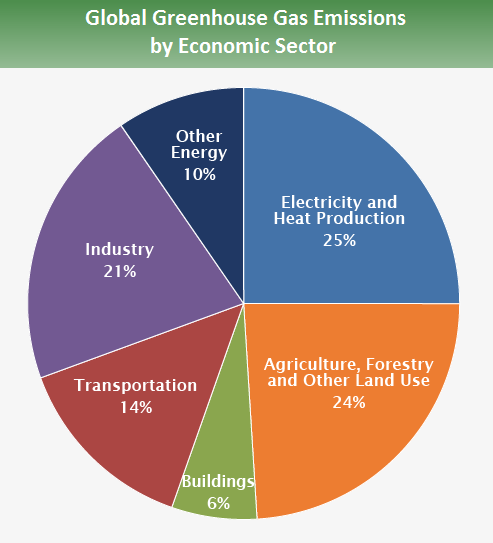
Climate change is a global phenomenon that has been driven by an increase in human-generated greenhouse gases emitted into our atmosphere, primarily due to fossil fuel burning for electricity and transportation. These emissions result in trapping more of the sun's heat in Earth's atmosphere, resulting in rising global temperatures.
Other factors contributing to climate change include population growth, land clearing and destruction of ecosystems, deforestation, energy consumption, and over-grazing. This decreases the amount naturally occurring carbon sinks that absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Natural forces such as changes in solar radiation can also contribute to climate change.
These human activities together result in Earth experiencing an overloading of its energy budget. This has caused an average global rise of 1° Celsius over pre-industrial time. As the oceans absorb most heat energy, glaciers melt more quickly than they form. Water scarcity, droughts, or extreme weather events such hurricanes and floods can also have devastating consequences.
To protect ourselves from further damage, it is essential for us to reduce our carbon footprint and start curbing our emissions now so that we have a fighting chance against the already significant impacts of climate change. Reducing our dependence on fossil fuels for electricity production is crucial alongside investing in renewable sources - think wind turbines or solar panels - which do not emit any harmful pollutants into the environment. You can also restore some balance in these delicate cycles of the planets that sustain us, such as reforestation.
What happens to developing countries when they experience the climate change effects?
Due to their limited access to healthcare and technology, developing countries and communities are especially vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Climate change can increase the pressure on already limited resources. Floods and droughts can also cause damage to already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can result in a reduction in crop yields. This will be disproportionately detrimental to poorer communities who are facing food insecurity. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
The long-term implications of climate change include continued resource scarcity, poverty, and health impacts including an increased number of vector-borne diseases such as malaria or dengue fever. There will also be an increased risk of flooding from rising sea levels, combined with extreme weather events. This puts lives at risk in coastal locations where many people lack the necessary infrastructure and emergency services to evacuate. Building resilience against these risks necessarily involves mitigating greenhouse gas emissions but may require other measures such as improved management of freshwater resources and better access to health facilities which assists with prevention strategies for diseases like malaria.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Incorporate Sustainable Practices Into Your Daily Life To Fight Climate Change
It is possible to integrate sustainable practices into every day life by reducing the amount of resources you consume, such as food and energy. You can shop secondhand or borrow items from friends and family instead of purchasing new items every day. In order to reduce the amount methane in the atmosphere, it is a good idea to eat vegetarian meals only once or twice per week. For energy conservation, remember to turn off the lights whenever possible when leaving a space.
The other way to combat climate changes is to reduce carbon emissions from transportation such as cars and aircrafts. You can also choose renewable power sources like solar panels to replace traditional fossil fuels and generate electricity at your home. To make climate change action effective, it is important to support policies that promote clean air regulations. Also, engaging with other citizens on issues such plastic pollution reduction and deforestation will help to create more conscious citizens that will take action.