
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental organisation that was established in 1988 as a part of the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP). It is a worldwide body that brings scientists, policymakers, researchers and others together to discuss and find solutions to climate change. The IPCC's mission is to educate the public about climate change and suggest possible solutions.
The Panel is made up of representatives chosen by governments. These representatives are selected by governments to be scientists in the IPCC meetings. Representatives recruit experts to help with the preparation of reports. You can nominate your own scientists to join the Panel. This practice does not necessarily mean that the government endorses a scientist's views.
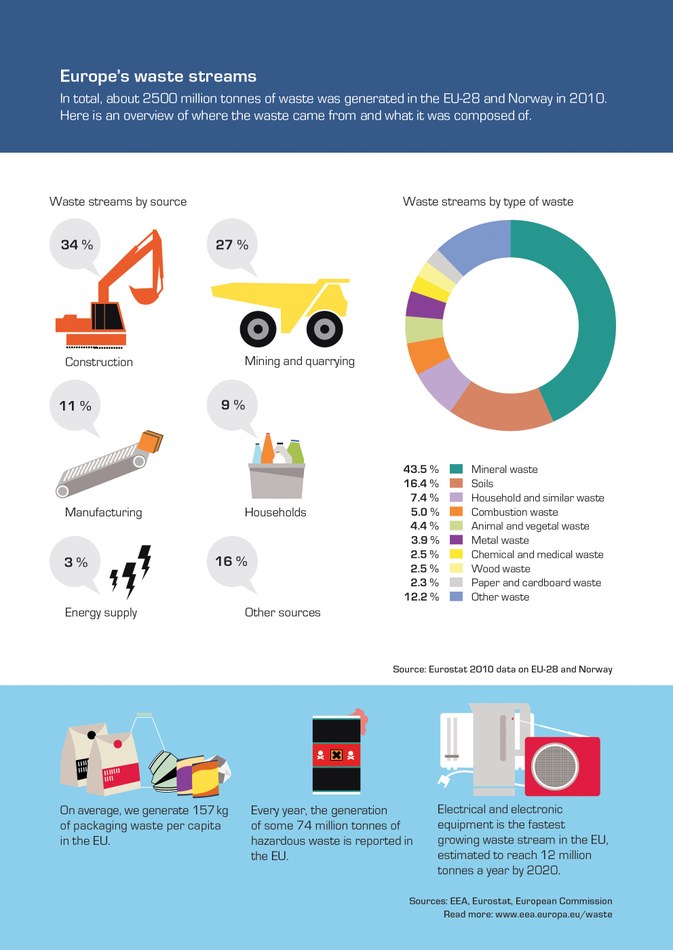
IPCC's structure consists of three groups that are focused on different aspects. One group works on the physical science, while the other two focus on adaptation and mitigation. Each working group is headed by a Cochair. Both Cochairs are also members the IPCC Bureau. They assist the chair with the selection of authors, and in preparing for meetings.
The Working Group I, the first of these groups, focuses primarily on the physical science behind climate change and its consequences. It includes the Met Office Hadley Centre which is one of the top climate research centres worldwide.
The Working Group II studies the impacts of climate-related changes on ecosystems and people, and proposes mitigation measures. The Australian Government is one of its members. It manages the DFAT Trust Fund, and contributes to IPCC decisions.
The third working group, the Working Group III, examines mitigation options and considers the impacts of climate change on the economic and social dimensions. It is made up of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), and other organizations.
The IPCC creates reports through volunteer groups made up of hundreds scientists from all around the world. They evaluate scientific literature and make recommendations based on the latest research. A comprehensive review of climate change knowledge is the IPCC assessment report. A report can be published in 4 parts.
A summary of the full IPCC report is called the Summary for Policymakers. This report is most often of interest to journalists and the general public. All IPCC reports are open to the public and can be reviewed by a range of experts. The IPCC collaborated closely with communication experts and practitioners to prepare the Fifth Assessment Report.
In February 2016, IPCC held an Expert Meeting on Communication. IPCC made many recommendations regarding how to communicate effectively at this meeting. Some of these guidelines were adopted into the IPCC’s outreach activities, and the IPCC website.
In September 2019, the IPCC published the Special Report of Ocean and Cryosphere under Changing Climates. The IPCC is currently preparing to release the Sixth Assessment Report (AR6). This comprehensive review of climate change knowledge will be released in September 2019. This report, as with previous assessment documents, will be distributed in parts.
FAQ
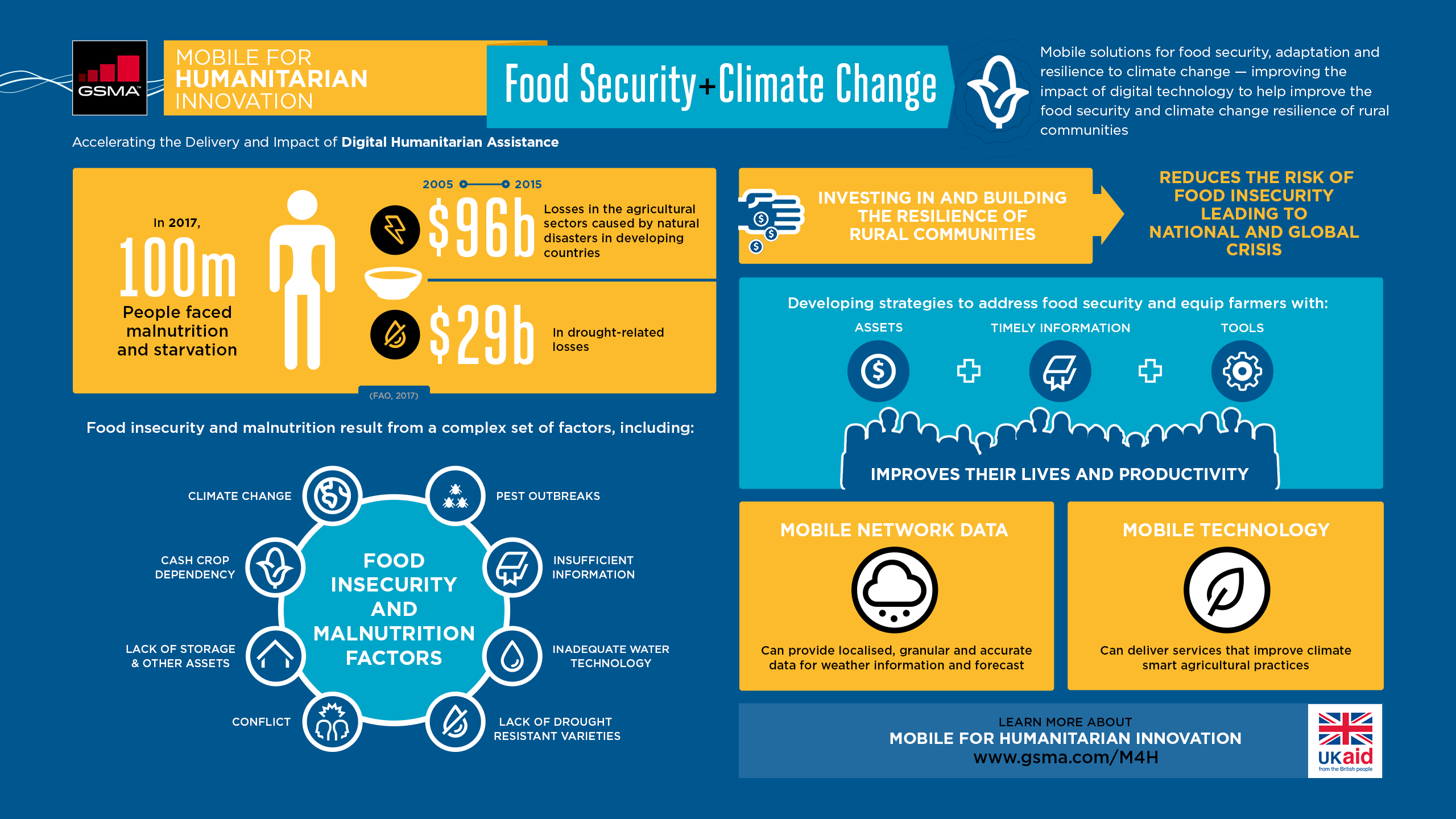
What does the role of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act like an invisible blanket surrounding the Earth, trapping the infrared radiation that warms it and keeping it from getting too hot. Without them the planet would be much more colder than it currently is.
These greenhouse gases are created by human activity such as burning fossil fuels. These activities are increasing in number, which means that more heat is trapped in our atmosphere. This can lead to extreme weather events and rising temperatures.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases (F-gases) are also major contributors to climate change.
Since preindustrial times, the concentration of greenhouse gases has risen significantly due to human activity. This has led to global warming and an increase in temperatures all over the world, as well as in our oceans. It is also leading to changes such as intense storms and droughts; melting glaciers; and rising seas.
To reduce further damage caused by climate change, human beings need to decrease their greenhouse gas emissions. We can do this by shifting away from fossil fuels in favor of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. You can also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reforestation and adopting farming methods that allow soil to absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These actions will help reduce atmospheric concentrations in greenhouse gases and create a healthier ecosystem for all life.
What are the environmental and social effects of climate changes?
Climate Change has wide-ranging effects on the environment as well society. Climate change is causing a variety of environmental problems, including rising temperatures, extreme weather, sea level rise, and reduced air quality. These changes can have severe consequences for human populations. They can lead to instability, increased poverty, insect-borne diseases and altered migration patterns.
Already, climate change is having an enormous impact on the environment as well as societies around the globe. This is expected to get worse as global temperatures continue rising.
Ocean levels rising due to melting ice caps is one of the most pervasive effects of climate change worldwide. This causes shoreline erosion along many coastlines and increases the risk of flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion can also happen, affecting freshwater supplies to coastal regions of many countries.
Climate change is causing extreme weather events like heatwaves, droughts and other severe weather to occur in many countries. These events lead to massive destruction of homes, businesses, and even the loss of whole communities. Additionally, severe storms pose additional risks due to flooding or landlides that can increase damage to infrastructure such roads and railways.
Climate change is also causing wildfires to become more frequent than ever before. This can have devastating effects on habitats as well as people living near them.
Many people are forced to flee their homes due to drastic changes in their living conditions.
Increased aridity also increases dust storms worldwide with unhealthy air pollution caused by these making it difficult for people who suffer from respiratory illnesses such as asthma especially vulnerable. Furthermore, pest infestations are predicted to rise in tandem with warmer temperatures. This phenomenon is known as the 'greenhousebug'. Global food insecurity will continue to grow as fewer crops have lower nutritional qualities. This could potentially lead to more hardships for people already struggling to make ends work.
What is climate change? How does it happen?
Climate change is the long-term shift in global weather patterns caused by an increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to global temperature rises that can result in a range of climate and weather changes. These include rising sea levels and melting glaciers, severe storms and droughts as well as widespread coral reef bleaching and species extinction.
Human activity is the main factor in climate change. This includes burning fossil fuels to generate electricity and transport, cutting down forests and raising livestock. The planet is heated faster when these activities release large amounts carbon dioxide (CO2) than natural processes, such as volcanic eruptions. These activities also produce more CO2 than volcanoes.
Another major contributor to the global greenhouse gas emission is deforestation. It accounts for around 15-20%. It releases the stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere when trees are chopped down or burned. Additionally, forests act a natural carbon source that absorbs CO2 into the atmosphere. Without this capacity, carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere will continue to rise with devastating effects for ecosystems around world.
Human-caused pollution not only releases CO2, but also other harmful gases like methane (CH4) or nitrous oxides (N2O). Methane has been extensively employed in industrial processes. It contributes significantly to the atmosphere's warming. While N2O can be emitted primarily by agricultural soil management activities, such as tilling or fertilization which release excess nitrogen to soil.
To minimize climate change humanity must make concerted efforts across social, economic, and political institutions to reduce these emissions drastically and transition away from our dependence on fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind power, or low-carbon hydrogen fuels. A smart approach to reducing atmospheric contamination and preventing CO2 accumulation could be to replace polluting fossil-fuel technologies with ones that encourage zero-waste living. We can take responsibility for how we impact the environment and begin to mitigate it. Preservation measures such as reforestation help preserve biodiversity while also absorbing large amounts of harmful CO2 back into the natural world. This is a powerful way to address climate change and restore balance for future generations.
What are the international efforts currently being made to address climate change
International efforts to combat climate change are moving at a remarkable pace and with unprecedented unity. Countries from all over the globe are increasingly coming together to find ways to reduce their emissions, increase resilience against impacts and invest in renewable energy.
The Paris Agreement is an international framework that encourages collective action. It also provides a framework to allow individual countries and regions to set voluntary targets to reduce emissions. The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change is also providing guidance to policy and piloting innovative initiatives, such as carbon market mechanism.
There are also progresses in certain regions. For example, the European Green Deal, a comprehensive package aimed at recreating Europe’s economy with sustainability at the core, and the African Renewable Energy Initiative, which targets increasing Africa's share in global renewable energy production, is being implemented.
There are many sectors and industries that are taking action in addition to policy development. Cities are making active transitions toward sustainable public transport systems, while society overall is adopting more sustainable lifestyles. Businesses are innovating technologies which reduce emissions, while investors move their capital from fossil fuels to renewables.
The OECD committee has adopted common standards to report national actions on climate change by rich countries. This is known as the 2021 Guidelines.
These efforts signify a new level of importance for climate action. If there is any hope of meeting the science-based Climate Goals, all stakeholders (governments, civil societies, and private sectors) must continue to build on their momentum and push for greater ambition & progress.
What is the current global climate? And how is it changing over time?
The current state of the global climate is one of unprecedented change and uncertainty. Temperatures are rising rapidly due to unprecedented levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide. This is causing heat waves, droughts, changes in rainfall patterns, melting of polar ice caps and ocean acidification as well as an increase in sea level.
These changes have already had a significant impact on ecosystems across the globe, leading to habitat loss and extinction. They are also threatening millions of people's lives and livelihoods, particularly in areas where there is already resource scarcity.
The number of extreme weather events - such as cyclones, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires - has been steadily growing over time due to higher average surface temperatures caused by human activity. This trend is expected to continue into the future as temperatures continue to climb.
Climate change has global consequences. It can affect everything, from food insecurity and displacement to communities that are forced to relocate due to severe weather events or rising sea levels. Climate change is also creating social inequalities bydisproportionately affecting marginalized populations that don't have the knowledge and resources necessary to adapt.
There has been progress in some areas, such as the reduction of carbon emissions or initiatives for renewable energy in certain countries. However, there is no global initiative that can be taken to effectively mitigate these changes. We must all work together now to stop further disruptions and destruction from climate change.
Statistics
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to incorporate sustainable practices into your daily life to combat climate change
One way you can incorporate sustainable practices into your daily life is by reducing your consumption of resources such as food, clothes, and energy. Shopping secondhand and borrowing items from family and friends is a better option than buying new products every day. Eating vegetarian meals at least once a week can reduce methane emissions from livestock production. To conserve energy, it is a good idea to turn off all lights when you leave a room.
Another way to fight climate change is by decreasing emissions from transportation sources like cars and airplanes through carpooling or taking public transit instead of driving alone. Renewable power sources, such as solar panels, can be used to replace traditional fossil fuels. It is crucial to support measures at the policy level that encourage clean air regulations in order to make climate change mitigation work. It is also a great idea to engage with others about issues like plastic pollution and forest destruction. This creates more informed citizens who will take action!