Climate change mitigation describes actions that are taken to keep the climate from changing. These actions include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, removing pollutants from the atmosphere, and improving energy efficiency. The first workshop, held in April 2019, was designed to identify the various mitigation options that could potentially be employed to address climate changes.
In October, another workshop was held. It aimed at assessing the well being effects of demand-side reduction options. A comprehensive literature review was conducted to assist with this task. It reviewed many approaches to assess the relationship between climate change mitigation, well-being, and other factors. It included the work of a group of experts, including well-being and technology experts, academics, and other professionals. To assess the well being of the scenarios, a cobenefit method was used.

Demand-side strategies are designed to influence the purchasing decisions of consumers and businesses. They change the demand for goods or services. These solutions are different from supply-side strategies, which concentrate on changing production technology, production processes or consumption patterns. These strategies are focused on increasing sustainability and promoting land and forest conservation.
Demand-side solutions can be divided into multiple categories. For example, the category "shift", which refers to a strategy to switch to low-carbon technologies, is one of these categories. Some of these strategies include increasing the availability of electric vehicles, developing more sustainable transport, or reforestation. Some strategies focus on reducing unnecessary consumption. But, to capture the behavioral consequences such actions have on our behavior, we need more modeling.
While most research has been conducted from a macroeconomic perspective, the social dimensions are often overlooked. More research should be done to understand how people's preferences, beliefs, and worldviews affect their decisions and the effects of climate change mitigation measures on their well-being. The relationship between the wide range of mitigation options, and the social constituencies that are relevant to them (such as people's social and economic well-being), is crucial research.
There are three main drawbacks to the joint assessment on climate change mitigation, well-being and wellbeing. First, the eudaimonic perspective, which emphasizes concrete conditions for a better life, isn't as prominent in the context of climate mitigation. Second, current assessment centres on GHG emissions have been limited to a macroeconomic perspective. Third, it is necessary to conduct more detailed research in order to understand how climate change mitigation options can affect well-being.
A team of nine experts conducted the first workshop. It involved a brainstorming session that identified potential demand-side solutions to climate change. Participants were divided into three categories: industry, infrastructure, as well as the health and wellbeing sectors. During the internal review, the upper boundaries of each of these three areas were defined in rounded numbers.
The workshop that dealt with the well-being aspect of demand-side reduction options also discussed the impacts of these policies on citizens' health. They also discussed the possibility of using the eudaimonic approach to evaluate well-being.
FAQ
How can human activity impact climate change?
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (IPCC), human activity is responsible for more that 70% of all global warming.
The release of carbon dioxide from fossil fuels: When fossil fuels are used, like coal, oil, or gas, they cause the atmospheric formation of carbon dioxide. This raises the already existing atmospheric levels of CO2 which acts as an "greenhouse gas", trapping heat from Earth's surface and increasing temperatures. This results in higher ocean levels because Arctic ice mellows and causes weather patterns to change around the world, which can lead to severe storms, droughts or floods. These could impact food production and pose a threat to human health.
Deforestation. Trees that absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in photosynthesis will be effected by being cut down. Reduced forest cover can also increase albedo, which is the amount of reflected sunlight coming back into space. This reduces solar heat absorption at the surface of the earth and promotes global warming. As well decreases local air quality with deforestation being linked permanently with respiratory issues.
Farming: Between 14% and 18% of global anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions are attributed to animal agriculture each year. Large amounts of methane gas are released by animal waste due to its richness in methane bacteria. Eating less or none of these products can reduce global warming.
In conclusion, although human activity has had a devastating impact on our environment for centuries, technological advancements have enabled us to focus our minds towards the future. Instead of relying on carbon-emitting heavy industry, we can use green innovation to create eco-friendly efforts that combat climate change effectively and ensure everyone's safety.
What is climate change and how does it occur?
Climate change is the long-term shift in global weather patterns caused by an increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to global temperature rises that can result in a range of climate and weather changes. These include rising sea levels and melting glaciers, severe storms and droughts as well as widespread coral reef bleaching and species extinction.
Human activity is the main factor in climate change. This includes burning fossil fuels to generate electricity and transport, cutting down forests and raising livestock. This is because these activities release huge amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. It warms the planet faster than natural processes like volcano eruptions.
Deforestation also plays a large role contributing about 15-20% of global greenhouse gas emissions. When trees are cut down or burned it releases their stored carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Furthermore, forests act like a natural carbon sink and remove CO2 from air. Without this absorption capacity carbon dioxide levels will continue rising with devastating consequences to ecosystems all over the world.
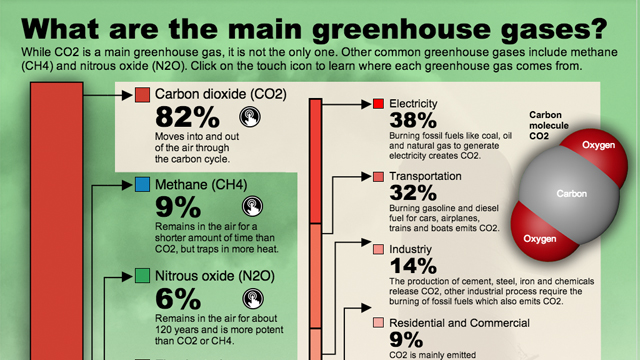
Human-caused pollution not only releases CO2, but also other harmful gases like methane (CH4) or nitrous oxides (N2O). Industrial processes have used methane extensively and it contributes to significant atmospheric warming. However, N2O is emitted mostly by agricultural soil management activities such as fertilization and tilling. These activities release excessive nitrogen into the soil which leads to N2O production when microbial contact occurs.
To minimize climate change humanity must make concerted efforts across social, economic, and political institutions to reduce these emissions drastically and transition away from our dependence on fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind power, or low-carbon hydrogen fuels. Smart solutions that encourage zero-waste living and replace polluting fossil fuels could help reduce atmospheric pollution and heat buildup. We can take responsibility for how we impact the environment and begin to mitigate it. Preservation measures such as reforestation help preserve biodiversity while also absorbing large amounts of harmful CO2 back into the natural world. This is a powerful way to address climate change and restore balance for future generations.
What can be done to ensure a sustainable future, given the climate change challenges?
Sustainability is the ability to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Climate change is presenting new challenges. We need to take immediate action to end our dependence on finite resources.
We must reexamine how we consume and produce energy, as well as our dependency on natural resources like fossil fuels, if we are to make a transition towards a more sustainable future. We must find new technologies, renewable resources of energy and systems that reduce harmful emissions while still meeting our daily needs.
Additionally, sustainability must be approached from a holistic perspective. This includes considering all aspects, such as the materials used and waste management. It also means incorporating energy utilization in transportation, industry, and industry. There are many possible solutions, such as the use of renewable energy like solar, wind, or hydropower; better waste management; increased efficiency of agriculture; improved transport networks; green construction regulations; and sustainable city planning initiatives.
To achieve this goal, we need to make behavioral changes in order for people from all walks of society to be successful. Education programs are required to educate people about climate change and show them how they can help create a more sustainable future.
Collaboration between government leaders, industry leaders, as well as citizens is the only way to make significant progress toward creating a more sustainable future for our children.
What are the possibilities for new technologies to combat climate change?
There are many technologies that can be used to tackle this global problem. From renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal to energy storage systems like battery packs or thermal tanks, advances in applied science are making it possible for us to transition to a more sustainable future.
New methods for carbon capture or sequestration can be used to lower greenhouse gases. Additionally, improved agricultural practices can reduce the emissions of livestock and soil erosion. Smart grid technology can be combined with existing power infrastructure to increase efficiency. Additionally, improved building design can reduce energy consumption.
Additionally, scientists can develop organisms using cutting-edge synthetic biological approaches to convert green sources of fuel like CO2 lasers into usable biofuels or alternate feedstocks. This could revolutionize transportation if the market turns away from petrol-based vehicles toward zero-emission electric cars powered by clean sources.
Finally, increasing investment in digital tech and AI can enable people to access data across borders and help them make more informed consumption decisions. Understanding our carbon production role is essential to help us all be better stewards.
How can the impact of climate change be reduced or mitigated?
There are many steps that can be taken in order to reduce and mitigate climate change's effects. These include reducing greenhouse gas emission through more energy efficient practices and using other sources of energy, improving land management practices, protecting forests, wilderness habitats, and protecting against extreme weather events like floods and droughts. Additionally increasing public education about climate change is also important as it encourages people to feel responsible for their actions.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to make your home more energy-efficient and combat climate change
Your home's energy efficiency is one of the most cost-effective ways to cut your carbon footprint, lower your utility bills, and improve your quality of life.
Make sure your home is well insulated and sealed. You must ensure that your windows and doors fit properly. If you find drafts around pipes or vents, make sure to add weather stripping and fill in any gaps with caulking around door frames and window frames.
Insulate walls, ceilings and floors for maximum energy efficiency. Inspect the attic for potential air leaks.
Lighting can account up to 18% for household electricity consumption. Switch to LED light bulbs to save up to 80 percent over traditional incandescent bulbs. By installing motion sensors or timers, you can save even more money by turning off lights when not required.
A newer model is more efficient and can help reduce your energy bills. A programmable thermostat can be used to set temperature settings based on the time people are at home and away.
All windows should be replaced by double-glazed units that are more energy efficient and less heat escaping. Low-flow showerheads are a great option, as they reduce water consumption but maintain adequate pressure.
ENERGY STAR rated devices use 50 % less energy than non-certified appliances. Don't forget about small details such as unplugging electronic devices like phone chargers or TV boxes when not in use - this could save you a significant amount of energy over time!
These are just a few of the steps that can dramatically reduce your impact on climate change and lower monthly electricity bills, making it easier to live at home.