
Education on climate change has the potential to have a major impact on the future and survival of the planet. A comprehensive education on the subject will not only increase young people's capacity to address climate change, but it can also reduce the negative impacts of a changing climate.
Educators must have the right tools and resources to help them incorporate climate change into their classrooms. They need to know what the curriculum should contain, how it should teach, and how it should assess. There are many resources for educators that can be used at no cost. These include videos and games as well as book recommendations.
Years of Living Dangerously contains a series interdisciplinary lessons which teach students about the impacts of climate change. Students are encouraged to examine the impact of climate change on the earth and find solutions. Along with science-based learning, the curriculum includes hands-on, writing projects and service learning opportunities. Educators can modify the curriculum to fit their specific needs.
The National Education Association supports the scientific consensus that global warming is primarily due human activity. This is a major cause of concern for both students and teachers. Columbia University's Center for Sustainable Development teaches students the many factors that affect Earth's climate. Students are encouraged to join local coalitions and advocate for change during the course.
The National Park Service's Climate Change Response Program provides a number of educational videos on the subject. For example, in the lesson "The Human Impacts of Climate Change", students learn about how a warming climate is affecting ecosystems and weather patterns. Videos can be accessed by educators in many languages.
You will find a large variety of resources at the Siemens Stiftung Media Portal, including interactive graphics and video clips. It is a great place for teachers to find a plethora of materials, such as worksheets and an abridged version of the IPCC report.
Teach Climate Justice seeks to educate young people about climate change and other issues. One of the campaign's members, an 18-year-old climate campaigner, has been campaigning since he was 13 years old. He wants to make significant changes to the school curriculum.
A shift in energy use is one of the most significant behavioral changes. A wealth of scientific research has shown how to reduce energy consumption and mitigate the adverse effects of warming.
Zinn Education Project's website has other useful resources. This includes free resources on climate change education. Teachers have access to videos, graphics, lessons, and can download a free copy the IPCC report.
Although teaching climate change is not without its difficulties, educators are making great strides. New Jersey was the first to adopt standards for educating teachers about climate change. Since then, many state-level learning standards were adopted. These include social studies, science, and world languages.
FAQ
How does the politics of climate change impact global efforts to address it?
Climate change has become a highly politicized topic that has caused great divisions among governments, nations, and individuals. The implementation of measures to address climate change is affected by the political stances of various actors. It is becoming difficult to reach consensus on global efforts for addressing this urgent environmental crisis.
Most scientists agree that humans are causing climate change. This is why it is urgent to act. Politics surrounding these issues can often hinder global cooperation, which is required to make effective progress in implementing sustainability energy practices and upholding regulations protecting natural environments, researching viable technological options, and other climate-change interventions.
Many governments in the world want to protect their economic interests, and enforce measures that limit business activities. This often conflicts with the regulations that experts recommend to address climate change efficiently. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
The difficulty of reaching a full consensus about the best way to combat climate change is further complicated by differences in power dynamics. Countries with more economic power often appoint their own representatives to represent them on international bodies responsible for negotiations over the environment - this can lead to lopsided discussions of those countries' perceived interests versus the collective interest of all involved parties. A number of potential side effects that could be caused by radical changes like geoengineering were also discussed at national and international levels.
At a grassroots level too, grassroots movements have struggled against powerful opponents including corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbies trying to maintain politically favorable positions for their industries especially when it comes to funding research into alternative forms of energy production or enforcing renewable energy technology mandates such as low emissions targets for vehicles etcetera - meaning individual governments must remain clearheaded about potential rewards and outcomes if they are going actively try to make valid progress on the matter in the question itself instead seeking public favor through short-term gains or even spectacles.
A coordinated effort to reduce our environmental crisis will only succeed if resources are distributed properly and there is no political divide between nations.
What does climate change mean for the oceans and marine life of the world?
What is the impact of climate change on the world's oceans and marine life?
Climate change has been significantly affecting the world's oceans and the associated marine life since its onset. The loss of the ozone coating and constant oceanic temperature increase causes significant disruptions in marine ecosystems.
Climate change can also be linked to unpredictable weather and stronger storms. This can cause extreme sea level rises that can prove fatal for coastal areas. Temperature changes can also cause water levels to drop, causing "dead zones", areas where there is less marine life.
Ocean acidification can also be caused by climate change. Excess carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere and accumulates in the oceans. Ocean acidification raises the pH balance which disrupts essential functions of animals unable to adapt such as oysters, clams, and crabs as their shells become weakened.
The effects of higher temperatures on natural habitats can be altered by shifting their geographical locations or shrinking them all together. This could lead to certain species becoming uninhabitable. This increase in ocean stress accelerates already high extinction rates amongst many species worldwide causing a severe imbalance between predators and prey that might eventually lead to complete extinctions.
All ecosystems are affected by climate change. This can be directly or indirectly via evaporation, water volume reductions or sharp temperature shifts. These changes could have a devastating effect on sustainable development of marine activities and fisheries. Global climate change continues to wipe out entire species of life on Earth, transforming our future lives not only on the land but also deep below the oceans' surface.
How can climate change be mitigated or reduced in its impact?
There are many ways to reduce or mitigate the impact of climate change. These include reducing greenhouse emissions by using greener energy sources and better energy practices. It is important to raise awareness of climate change in order to encourage people and make them feel responsible for their actions.
What is the role of greenhouse gases in climate change?
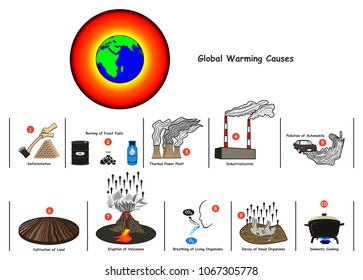
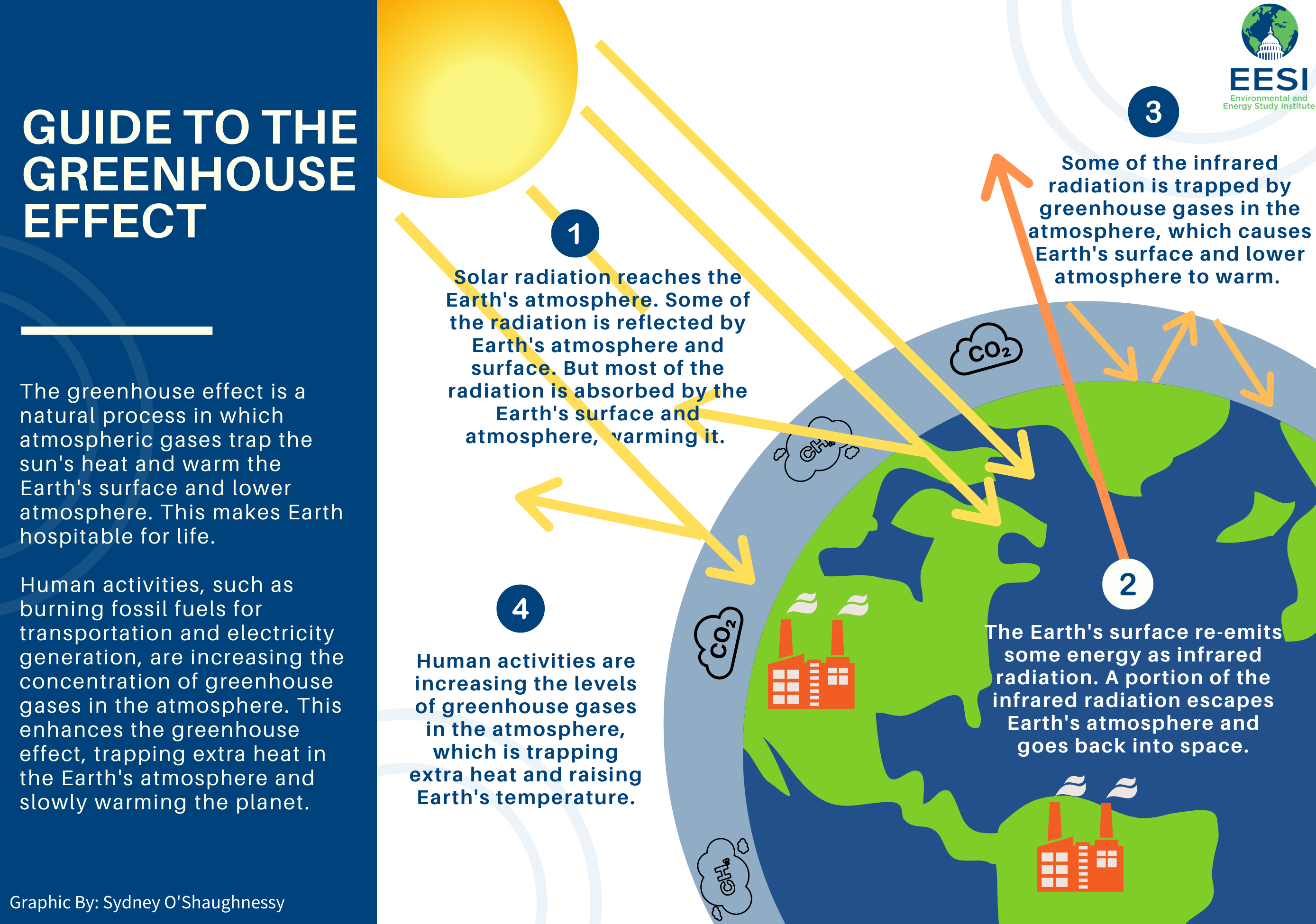
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act as an invisible blanket that wraps around the Earth, trapping heat radiation and warming it. Without them the planet would be much more colder than it currently is.
Human activity can cause greenhouse gases, such as the burning of fossil fuels and other industries that emit emissions. As more heat enters the atmosphere from these activities, it leads to increased temperatures and extreme weather.
The most prevalent greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide, which is released from fossil fuels, such as oil, gas, and coal. Other major contributors to climate changes include methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Since preindustrial times, the concentration of greenhouse gases has risen significantly due to human activity. This has led both to global warming and an increase worldwide in temperatures, as well as increased ocean levels. It is also leading to changes such as intense storms and droughts; melting glaciers; and rising seas.
To avoid more damage from climate changes, humans must reduce their emissions by switching away from fossil energy to increase their use of renewable energy like solar and wind power. Reforestation and other agricultural practices can be used to absorb more CO2 from air. These activities will help lower atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases and create a healthier environment for all life on Earth.
What is the relationship between climate change and extreme weather events?
Extreme weather events, such as heat waves, floods, droughts, cyclones, storms, and hurricanes are directly linked to global warming. Global warming has caused an increase in atmospheric temperatures. This has had an impact on different weather phenomena worldwide.
According to climate scientists the average frequency for extreme weather-related events has increased more than twofold since 1980. Rising ocean water temperature causes sea levels to go up as well as changing wind patterns. This affects the normal distribution of storms and hurricanes in different geographical regions across the planet.
The 2015 El Nino event pushed warm water toward South America resulting in rising temperatures at an alarming rate along with heavy rains that triggered floods in Peru and Bolivia resulting in the displacement of people and property damage. Several places including Antarctica have recorded their highest-ever temperatures indicating a definite relation between global warming trends and the occurrence or frequency of extreme weather events around the world.
Another example is Hurricane Irma, which struck in 2017, causing $50 billion in economic damage not only to Florida, but also to other states like Puerto Rico, Cuba, and others. This proves once again that climate change has been responsible for an increase in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concluded that human activities are increasing the severity of current climate change which naturally leads to more frequent, severe, and intense natural disasters globally hence bringing forth strong evidence regarding humans' relation to extreme weather events occurring at frequent intervals around us all.
What is climate and how does it affect us?
Climate change is the long-term shift in global weather patterns caused by an increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which causes global temperatures rise. This leads to many changes in weather and climate. These include rising sea levels and melting glaciers, severe storms and droughts as well as widespread coral reef bleaching and species extinction.
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. These include burning fossil fuels, transporting electricity, cutting down trees, and farming livestock. These activities cause the atmosphere to heat up much faster than natural processes, like volcanic eruptions. They also emit many times more carbon dioxide than volcanoes.
A large part of the global greenhouse gases emissions is also caused by deforestation. When trees are cut down or burned it releases their stored carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Forests also act as a natural carbon sink, removing CO2 from the atmosphere; without this absorption capacity, carbon dioxide levels around the globe will continue to rise, with disastrous consequences for ecosystems.
Human-caused pollution not only releases CO2, but also other harmful gases like methane (CH4) or nitrous oxides (N2O). Industrial processes have used methane extensively and it contributes to significant atmospheric warming. However, N2O is emitted mostly by agricultural soil management activities such as fertilization and tilling. These activities release excessive nitrogen into the soil which leads to N2O production when microbial contact occurs.
To limit climate change, we must collaborate across economic, political, and social institutions in order to reduce our emissions and transition away fossil fuel dependence towards renewable energy sources. Smart solutions that encourage zero-waste living and replace polluting fossil fuels could help reduce atmospheric pollution and heat buildup. Reforestation projects, which are powerful aid in the fight against climate change by absorbing large quantities of CO2 back into nature and maintaining biodiversity, can help us take responsibility for our environmental impact.
What can we do to help the climate change process?
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Changes (IPCC), more than 70% global warming has been caused by humans since the middle of the 20th century.
The release of carbon dioxide from fossil fuels: When fossil fuels are used, like coal, oil, or gas, they cause the atmospheric formation of carbon dioxide. This will increase the atmospheric CO2 levels already present. It acts as a "greenhouse gases" by trapping heat in Earth's atmosphere, increasing temperatures even more. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation: Trees that sequester atmospheric CO2 in their trunks during photosynthesis are destroyed by deforestation. The albedo is also increased by cutting down forests. It refers to the amount of solar radiation reflected back into space. Deforestation is also associated with respiratory problems and local air quality.
Farming: Between 14% and 18% of global anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions are attributed to animal agriculture each year. Because of its high methane content, animal waste emits large amounts methane into the atmosphere. Reducing your intake of animal products is an effective way to lower your greenhouse gas emissions. Nitrous oxide can also be released into our atmosphere. This creates smog that harms our respiratory system.
Conclusion: Human activity has had a profound impact on the environment for centuries. However, technology has made it possible to leverage green innovation and make eco-friendly efforts to combat climate change. This will ensure that everyone is safe while prospering in nature.
Statistics
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to Invest Clean Energy to Support a Low-Carbon Transition
Clean energy is any form of renewable energy that doesn't produce or emit pollution. It includes technologies such a solar photovoltaic (Solar Photovoltaic), wind power, hydroelectricity and geothermal energy. Investing in clean energy sources can have many environmental benefits, such as reducing reliance on fossil fuels, reducing the amount of air pollution generated by traditional electricity methods, and providing more reliable electrical access to remote locations.
By buying shares in companies involved in developing clean energy technologies, investors can get involved in these projects. This includes investing in publicly traded stocks, mutual funds and ETFs (exchange traded funds) that are related to renewable energy. Investors may also be interested in direct investments in start ups or venture capital projects that fund research and technology development.
Clean energy investment is a way to support innovation and reduce harmful emissions. This investment may lead to economic growth by creating jobs related the production of renewable energies that require skilled labor. The tax incentives programs that encourage investment into green technologies such as wind farms and solar panels can also provide investors with a financial reward.
By investing in companies that produce electricity from renewable sources such as sun, wind and water, while avoiding any activities that might harm the environment, you can help support the transition towards a low-carbon future, while also reaping economic benefits.