
Earth is the only planet in the solar system known to have life. But how did life start on Earth? Scientists believe that the first forms of life evolved on Earth in the very early days before it was fully developed. Scientists also believe that there may be more species of life on Earth than is currently known.
A supply of liquid water is crucial for human life. This is accomplished through the water cycle which includes three phases. While the oceans are the largest body of water on Earth, there are large lakes as well as rivers. Aquifers underground also contain liquid water.

As the Earth warms up, chemicals rise to surface and form the atmosphere. Radioactive elements are released heat when they decay. Some of this heat can be stored in the Earth's deepest core. Organisms can also release radioactive elements to the atmosphere. Scientists believe the outer core's temperature is between 6,700 and 7,800 degrees F. However the inner core could be much hotter.
Methanogens produced high levels of methane during the early days of our existence. These methane molecules helped screen ultraviolet light waves from reaching the surface, allowing for the formation of the ozone screen. A few decades later, organisms began appearing on the Earth's crust.
These changes led to the Earth's changing surface. Eventually, rain started to fall. The seasons also changed. This was due the uneven heating caused by the sun.
In the end, the sun would be a red giant. The Earth would become more spherical due to its gravitational force. When this occurred, the equator pointing toward the sun and the North and South hemispheres pointing away from the sun.
Another major impact that struck Earth in a huge explosion caused a significant change on the planet. This resulted in some of its raw materials being ejected to the surface. The majority of heavier stuff fell to its center, while lighter items rose to the summit. At that time, most of the earth was liquid.
Earth is round today and has the shape of a doughnut. While its diameter is about 12,700 kilometers (7,900 miles), its circumference is greater at the equator. Depending on the speed with which you're traveling, you can reach the center of the planet in about five to seven kilometers.
The lithosphere, as well as the mantle, make up 84% each of the planet's volume. The lithosphere consists of heavy rocks while the mantle consists of molten rock. The Earth's surface is 80-550 kilometers high, and the lithosphere lies at that elevation.
The mantle is made of rock that has been melted down during volcanic eruptions. The mantle pressure increases as the Earth's temperature increases. The molten rock is forced to the surface. The volcano's eruptions produce lava that is released, which heats the surface.
FAQ
How can human activity impact climate change?
Human activity is one of the major factors contributing to climate change. In fact, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), humans are responsible for more than 70% of all global warming since the mid-20th century.
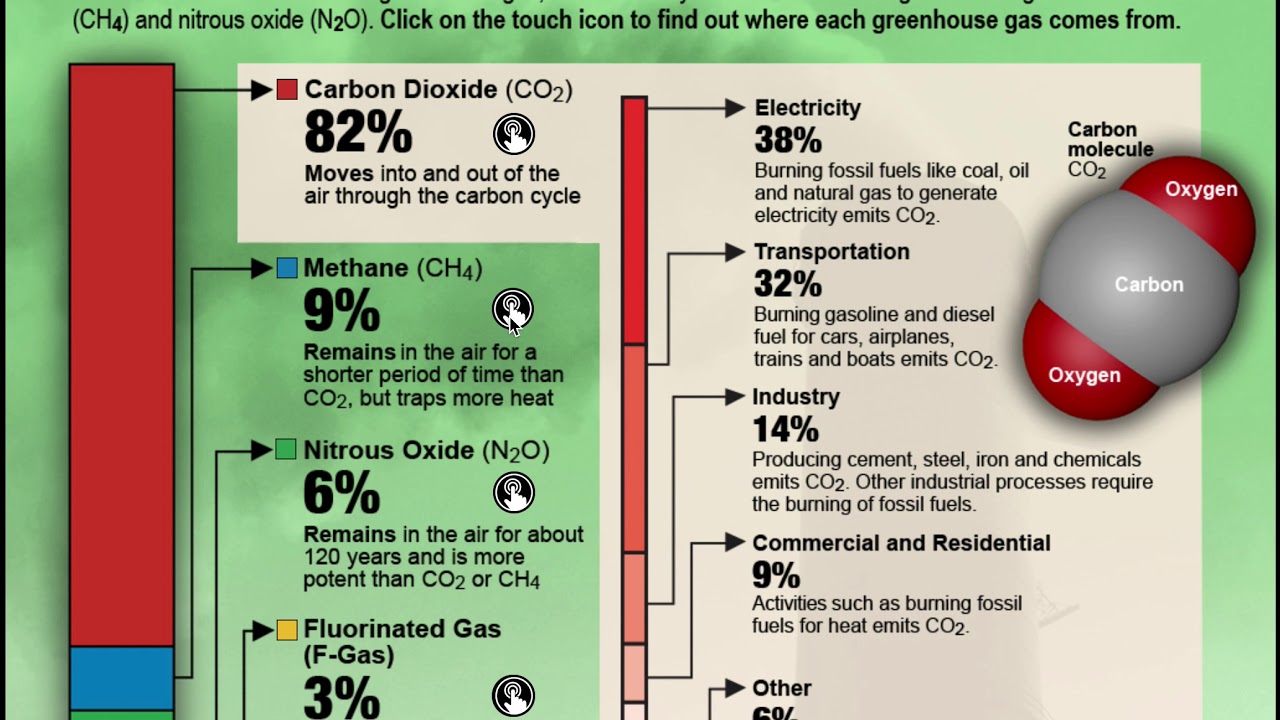
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This will increase the atmospheric CO2 levels already present. It acts as a "greenhouse gases" by trapping heat in Earth's atmosphere, increasing temperatures even more. As Arctic ice melts, this causes ocean levels to rise and can cause severe weather patterns all over the globe, including floods, droughts and storms that could lead to food shortages.
Deforestation: Trees that sequester atmospheric CO2 in their trunks during photosynthesis are destroyed by deforestation. The albedo is also increased by cutting down forests. It refers to the amount of solar radiation reflected back into space. The deforestation of forests can also affect the local air quality, which is directly linked to respiratory problems.
Farming: Animal agriculture accounts for between 14%-18% worldwide's total anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. Due to the high levels of methane bacteria in animal waste, methane gas is released into the atmosphere in large quantities. Changing your diet to less or no animal products can help reduce this contribution. Smog from ground-level ozone can harm our respiratory system and make our lives more hazardous.
In conclusion, although human activity has had a devastating impact on our environment for centuries, technological advancements have enabled us to focus our minds towards the future. Instead of relying on carbon-emitting heavy industry, we can use green innovation to create eco-friendly efforts that combat climate change effectively and ensure everyone's safety.
What's the current climate in the world? And how does it change?
The global climate is currently experiencing unprecedented uncertainty and change. Temperatures are rising rapidly due to unprecedented levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide. This is causing heat waves, droughts, changes in rainfall patterns, melting of polar ice caps and ocean acidification as well as an increase in sea level.
These changes have already had a significant impact on ecosystems across the globe, leading to habitat loss and extinction. These changes are also threatening billions of lives and livelihoods, especially those living in areas of resource scarcity or poverty.
Because of the increase in average surface temperatures from human activity, the number of extreme weather phenomena such as hurricanes and cyclones has been increasing steadily over time. As temperatures continue their climb, this trend is expected to continue.
Global climate change is causing many problems. These include rising food insecurity, displacement due to extreme weather events and sea level rise that force communities to move. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
Although there have been some progress in efforts to reduce carbon emissions and renewable energy initiatives in certain countries, it is still not clear that meaningful global action is required to mitigate these changes. To prevent further destruction and devastation caused by climate change, all countries must work together to take immediate action and plan for adaptation in an ever-changing world.
How are extreme weather events related to climate change?
Global warming is directly responsible for extreme weather events such as heat waves and floods, droughts. Cyclones, storms and hurricanes are all a result of global warming. Global warming has caused an increase of atmospheric temperatures.
According to climate scientists in 1980, extreme weather-related natural disasters have increased by more than twice the rate. As the ocean temperature rises, so does the frequency of extreme weather-related disasters. This impacts the normal distribution of storms or hurricanes in different areas across the globe.
The 2015 El Nino event pushed warm water toward South America resulting in rising temperatures at an alarming rate along with heavy rains that triggered floods in Peru and Bolivia resulting in the displacement of people and property damage. Many locations, including Antarctica recorded their highest ever temperatures. This shows that there is a clear relationship between global warming trends with the occurrence or frequency extreme weather events.
Another example of climate change at work is Hurricane Irma. It was a major storm that struck Florida in 2017, causing economic losses of $50 billion.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concluded that human activities are increasing the severity of current climate change which naturally leads to more frequent, severe, and intense natural disasters globally hence bringing forth strong evidence regarding humans' relation to extreme weather events occurring at frequent intervals around us all.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce Your Carbon Footprint & Fight Climate Change
There are many things you can do to help reduce your carbon footprint, and fight climate change. First, you can reduce your energy consumption by purchasing energy-efficient appliances, lighting and insulation. You can also cut down on energy by not plugging electronics, using public transport, walking, and lowering the temperature in winter and summer.
Second, recycle as much material as possible. Compost food scraps rather than throwing them away. This will ensure that they don't end-up in landfills which release methane gas into our atmosphere. Third, plants trees around your house for shade and natural cooling. The air absorbs carbon dioxide through the vegetation. Finally, consider purchasing products with minimal packaging or sustainable labelings such as organic cotton or FSC-certified wood which means it's been sustainably managed over time to ensure forest health.
Not only can you reduce your personal emissions but you can also support organizations like The Nature Conservancy Canada, Climate Change Solutions and Emissions Reduction Alberta.
We can all make small changes in our daily lives to combat climate change!