
A cryosphere is an area of Earth's surface which includes ice sheets and ice caps, sea-ice, lake ice and river ice. It is an integral part of the climate system. Cryosphere changes include changes to temperature, precipitation, or circulation. This area provides water resources for ecosystems. It also plays a crucial role in controlling ocean currents. In addition to these effects, it is a major source of methane.
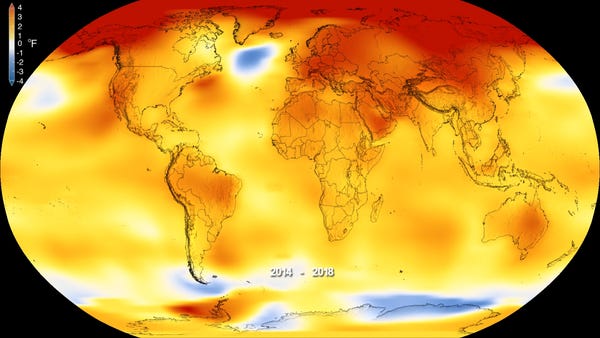
Many areas of the cryosphere remain unstudied. Many types of ice and snow cover much of the Earth's surface, including the Arctic and Antarctica. The snow cover can block the energy cycle by acting as an insulator. This effect is not always uniform. Certain Arctic regions have a higher level of albedo than others. These darker surfaces absorb more sun. As the planet warms, these areas will thaw.
Sea level will rise because of the melting of ice, snow, and other ice. This is a serious problem. It will affect all of the communities that live near the coastline. It will also cause acidic oceans to increase. Losses of ice mass will also affect mid-latitude weather. The marine ecosystems that provide food for the entire world will be affected by changes in the oceans. Also, warmer temperatures may allow for longer Arctic growing seasons.
The rate of warming will be affected by sea ice loss and permafrost melting. Research has shown that if we continue to burn fossil energy at the current rate, we can expect to see a quarter of permafrost to melt by 20100. That's more than a doubling of the current Arctic contribution to global warming. At this rate, melting ice will have a bigger impact on the world. Even if we quit burning fossil fuels by tomorrow, warming impacts will still occur, particularly in coastal regions.
Permafrost has a significant carbon content. If it thaws, it releases a huge amount of methane, which is a greenhouse gas. A thaw might also result in the decay and death of frozen organisms. These processes will accelerate the rate that methane is released. Permafrost can release between 300 and 600 million tonnes of net carbon every year if it is thawed.
In layers of ice, glaciers and other ice, you can find detailed records about past climate. Furthermore, it has been estimated that permafrost may be the second-largest natural source of carbon on the Earth after the atmosphere. Permafrost currently contains approximately one-and-a half billion tons of carbon. This number will reach more than three billion by the end this decade.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change released recently a special report on how climate change is affecting land and oceans. While most of the cryosphere remains unstudied, it is an important indicator of climate change in the future. They concluded that the world's oceans are crucial to the health and well-being of the planet. The impact of these changes on the planet will affect everyone.
FAQ
What happens to developing countries when they experience the climate change effects?
Due to their limited access to healthcare and technology, developing countries and communities are especially vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Temperature, precipitation and sea level changes increase pressure on already finite resources. Already fragile ecosystems are being destroyed by floods or droughts. Rising temperatures can reduce crop yields. This will impact communities with low incomes and food insecurity. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and heatwaves, can cause the destruction of infrastructures and displacement of people, which further perpetuates economic inequality.
The long-term implications of climate change include continued resource scarcity, poverty, and health impacts including an increased number of vector-borne diseases such as malaria or dengue fever. A rising sea level and extreme weather events will increase the risk of flooding, putting lives at stake in coastal areas that often lack the infrastructure or emergency services required to evacuate. These risks can be mitigated by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, other measures may be required such as better management of freshwater resources or easier access to healthcare facilities that aid in the prevention of diseases like malaria.
What are some of the proposed solutions to climate change and how effective are they?
Climate change is a critical issue of our time, and requires the urgent attention of governments, businesses, citizens, and all other stakeholders. Climate disruption is obvious by rising temperatures, melting polar ice, extreme weather, higher sea levels and increasing sea levels. Many solutions have been offered to this problem, ranging from technological and behavioral solutions to geoengineering.
Technological Solutions. A variety of technological solutions have emerged to combat climate change. These include renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power which provide reliable sources of clean energy with minimal side effects on the environment. Electric cars powered with renewable energy could dramatically reduce pollution in cities and replace petrol vehicles. Other technological solutions include projects to increase carbon sequestration within trees and soil, as well coastal protection systems that protect vulnerable places from rising oceans.
Behavior Changes: Making small changes to your routines can make an enormous difference in reducing carbon emissions and limiting the likelihood of future climate disruption. For example, local production of goods and shorter supply chains can help reduce the emissions associated with transport costs. The use of public or active transportation, as well as reducing cost and air polluting simultaneously, is a good option. In the same way, better insulation in your home can help reduce dependence on gas boilers that heat your homes.
Geo-engineering : Geo-engineering refers to large-scale interventions in natural system that have been deemed too risky for potential unforeseen results.
The effectiveness of these solutions largely depends on how much producers commit themselves towards investing in green alternatives; currently, initiatives such as using electric Cars tend expensive when compared with petrol versions however economic incentives favoring green investments play an integral role in incentivizing alternative solution uptake otherwise these remain mostly dormant when exposed only market forces which cannot guarantee their utility over time try apart from increasing consumer awareness over time regarding their efficiency hence mandating alternative solutions via policy measures represents one way forward however this needs regulatory bodies willing committed enough engaging players involved further still nontechnological approaches work one level but solving global warming phenomena requires all parties involved tackling issue earnest together.
Is there any potential for new technologies that address climate change?
The potential of new technologies to address this global challenge is vast. Advances in applied science make it possible to move to a more sustainable future.
To reduce greenhouse gas emissions, new methods of carbon capture can be used. Enhanced agricultural practices can also help to reduce the amount of livestock and soil degradation. Smart grid technology can also be used with existing power infrastructure for an efficiency boost, and improved building design can help minimize energy consumption.
Additionally, scientists can develop organisms using cutting-edge synthetic biological approaches to convert green sources of fuel like CO2 lasers into usable biofuels or alternate feedstocks. This could revolutionize transportation if the market turns away from petrol-based vehicles toward zero-emission electric cars powered by clean sources.
Finally, greater investment in digital technology and AI can help empower people across borders with greater access to data on their ecological footprint and ultimately lead to more informed choices regarding consumption habits. Understanding how we contribute to the carbon production of our planet is key for better stewardship.
What is the relationship between climate change and extreme weather events?
Extreme weather events, such as heat waves, floods, droughts, cyclones, storms, and hurricanes are directly linked to global warming. Global warming has led to increased atmospheric temperatures.
Climate scientists claim that the frequency of extreme weather related disasters has more then doubled since 1980. Sea levels rise as a result of changing wind patterns and ocean temperatures. This alters the normal distributions of storms, hurricanes, and other weather phenomena in different geographical areas around the globe.
The 2015 El Nino event caused warm water to move towards South America, leading to rising temperatures at alarming rates and heavy rains that caused floods in Peru (and Bolivia) causing property damage and displacement. Many locations, including Antarctica recorded their highest ever temperatures. This shows that there is a clear relationship between global warming trends with the occurrence or frequency extreme weather events.
Another example is Hurricane Irma. In 2017, it caused $50 billion of economic losses not just in Florida, but also in other states like Puerto Rico, Cuba and Puerto Rico. This shows that climate change is responsible again for the dramatic rise in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concluded that human activities are increasing the severity of current climate change which naturally leads to more frequent, severe, and intense natural disasters globally hence bringing forth strong evidence regarding humans' relation to extreme weather events occurring at frequent intervals around us all.
What is the contribution of human activity to climate change?
Human activity is one of the major factors contributing to climate change. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (IPCC), human activity is responsible for more that 70% of all global warming.
Burning Fossil Fuels: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This adds to already existing levels of atmospheric CO2, which act as a "greenhouse gas" by trapping heat from the sun in Earth's atmosphere and increasing temperatures even further. As Arctic ice melts, this causes ocean levels to rise and can cause severe weather patterns all over the globe, including floods, droughts and storms that could lead to food shortages.
Deforestation: Deforestation knocks out trees which sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks when they take it up during photosynthesis. Cutting down forests also increases albedo - the amount of reflected solar radiation coming back into space - reducing solar heat absorption by the earth's surface thus promoting excessive warming at the global level. As well decreases local air quality with deforestation being linked permanently with respiratory issues.
Farming: Between 14% and 18% of global anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions are attributed to animal agriculture each year. Large amounts of methane gas are released by animal waste due to its richness in methane bacteria. Eating less or none of these products can reduce global warming.
In conclusion, human activity has been drastically impacting our environment for centuries now, but with rapid advances made in technology such as renewable energy sources availability we have started turning our heads towards the future leaving behind carbon-emitting heavy industries results will soon start speaking themselves clearly when we leverage on technology through green innovation paving away toward eco-friendly efforts combatting climate change efficiently keeping everyone safe under prosperous nature purview.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to educate your community about climate change and mobilize action
There are many ways to learn about climate change education, including online resources and interactive tools, classroom activities, simulations and experiential learning programs. The key elements of effective climate change education are:
-
arming people with practical knowledge about the subject
-
Demonstrating how individuals can make a difference
-
Engaging participants in an open discussion about possible solutions
-
Inspiration through shared experiences that inspire action
Teachers can help communities to reduce their environmental footprints by offering comprehensive lessons in climate change for both adults and students.
Moreover, connecting scientific research with real-world examples offers a unique way to engage audiences in a meaningful dialogue. Participants also have the opportunity to observe positive outcomes and learn from them, which can lead to further innovation or replication within their organizations.
By incorporating action-oriented activities into education curriculums, participants are equipped with the mental tools necessary to create campaigns or petitions. They can then become agents of change in their communities or for sustainability. A focus on individual agency emphasizes the importance and benefits of participation in reducing carbon emissions. However, it also highlights participants' collective contribution to a larger end result. Involving stakeholders early in the decision-making process encourages them to be involved. This could lead to more equitable outcomes for all those affected by policy design decisions. We might be able, together, to increase public awareness of the effects of climate change and take appropriate action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.