
In managing climate change impacts, resilience is key. It is the ability of a system and its capacity to respond to adverse events. This term often refers to the resilience of buildings. These efforts are designed to minimize risks associated buildings, supply chains, or other infrastructure. These efforts are usually carried out by policy makers and decision-makers. However, achieving resilience is complex. This article discusses the definition of resilience, its implementation in the sector of building, and how it's measured. These insights help stakeholders to identify adaptation opportunities and make informed decision.
In many academic domains, climate resilience has been studied. A strong focus has been placed on cities' resilience to climate change. These strategies include increasing the resilience of buildings to specific hazards like flooding and seismic activity. These strategies are also designed to increase emergency responses and decrease recovery times.
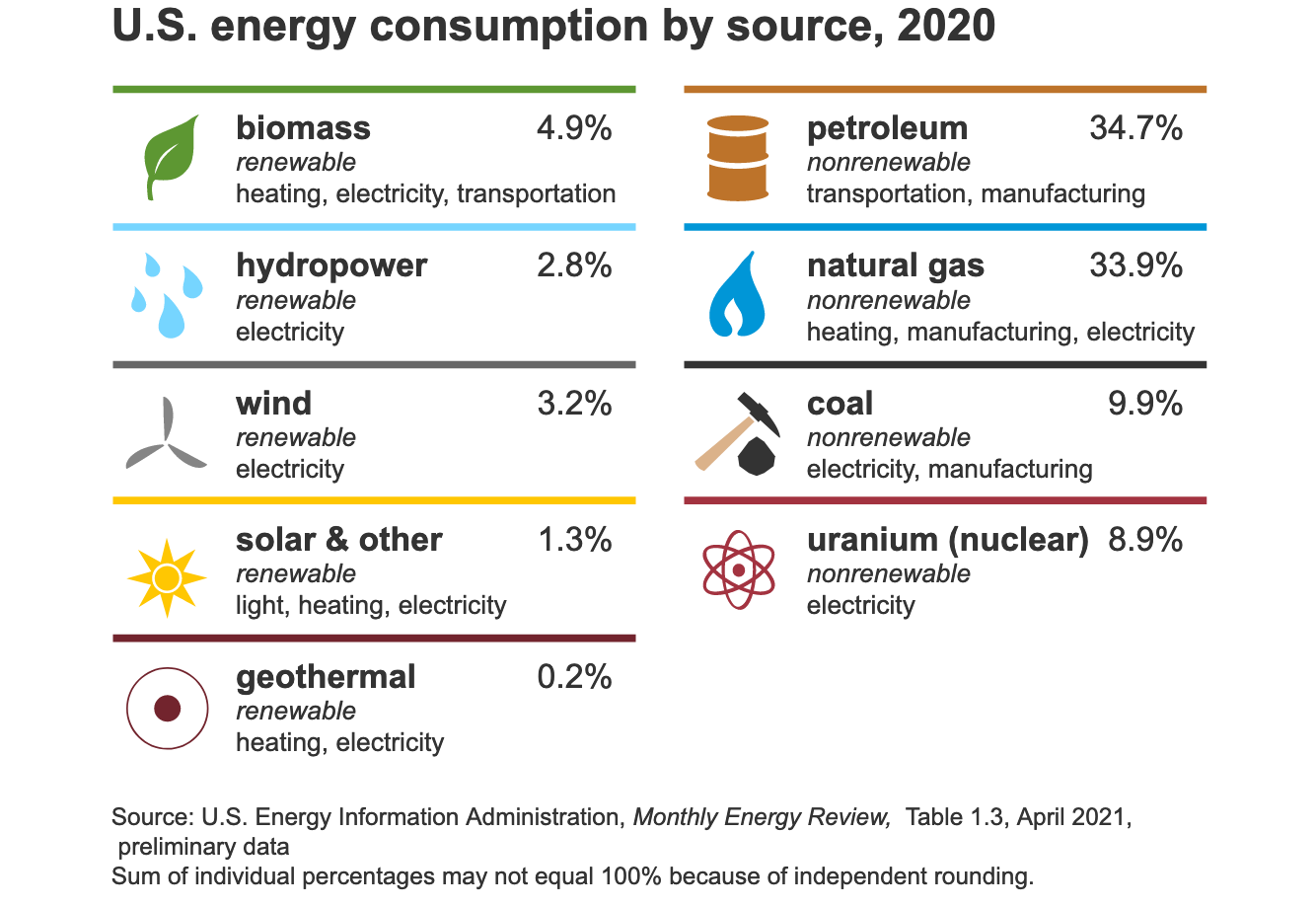
Resilience is defined as the ability to maintain essential processes and structures by ecological research. For example, a resilient environment built can be more resilient to extreme natural hazards like floods or hurricanes. This definition is simple, but it represents the current state of resilience knowledge.
Another focus area is resilience in social sciences. This domain examines the interaction of system components such as communities and identifies key roles that government, business and individuals can play. One strategy to improve resilience is strengthening social cohesion, and community empowerment. Even though this strategy isn't well understood, it does point to the importance of adaptation efforts.
Another option is to develop alternative interventions like solar panel kits. These can be more economical than rebuilding, especially when you are in low-resource environments. Yet, there are limitations to these techniques. These techniques might not be suitable for remote and difficult-to reach areas.
Diverse efforts to improve climate resilience are also characteristic of their success. For example, The Northern Institute of Applied Climate Science (NIACS) has incorporated traditional ecological information into its work. There are many international groups that support resilience such as the Adaptation Research Alliance. All of these initiatives are designed to share best practices, develop metrics, and mobilize countries.

Finance is the third major focus area. Through the Executive Order on Tackling Climate Crisis, the United States is trying to increase resilience finance. This includes coordination among different departments and agencies. In the same vein, the United Kingdom will place additional emphasis on adaptation in 2021 at the G7 Summit.
Finally, the social sciences have a strong literature on resilience that addresses factors that affect climate change responses. Some studies have focused on resilience theoretical frameworks. Some studies have examined the impact of resilience on economic and social well-being. While most studies have focused on disaster risks reduction, social science has explored other resilience strategies.
As strategies and resilience approaches develop, it is important that professionals understand the implications of different definitions. The ability to understand the differences between the definitions can assist stakeholders in choosing the right approach for each situation.
FAQ
How can developing countries and communities cope with the effects of climate changes?
Because of their limited access and lack of technology and healthcare, the impact climate change has on developing countries and communities is particularly severe. Climate change can increase the pressure on already limited resources. Floods and droughts can also cause damage to already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can lead to a decrease in crop yields, which will disproportionately affect poorer communities struggling with food insecurity. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
Climate change has long-term consequences. They will lead to continued resource scarcity, extreme poverty, and adverse health effects, including increased incidences of vector-borne illnesses like dengue fever and malaria. Additionally, flooding will become more common due to rising sea levels and extreme weather. These risks can put lives at high risk in coastal areas with a dearth of infrastructure or emergency services. While mitigating greenhouse gases is essential to build resilience to these risks, there are other options available. These include better management of freshwater resources and easier access for health facilities. This helps with the prevention of diseases such as malaria.
What is the role of individuals and communities in addressing climate change?
Climate change is one of the biggest contemporary challenges we face today. It is a major issue that affects everyone. Individual action and collective attention are needed to make an impact.
Individuals have a crucial role in helping to address climate change and reduce its effects. A person's everyday behavior can range from cutting down on waste and conscious consumption to making lifestyle changes such as changing to vegetarianism or using public transportation less often and choosing eco-friendly clothing and home decor. They can also take part in advocacy and support initiatives that promote sustainability in their communities.
They are also crucial in addressing climate issues on a wider scale. They can also implement policies to reduce emissions, such as promoting electric and bicycle transportation, encouraging the use of efficient infrastructure, reducing deforestation, and encouraging waste management systems. This mission requires collaboration between communities in different cities and countries.
Civic education regarding climate change is essential from the beginning of education and throughout the lifelong learning process. This will make individuals more aware of the problems and help them understand the interconnectedness with societies farther away than their own.
Ultimately employers have a major responsibility when it comes to fighting climate change: introducing corporate practices focused on sustainability and opting for green alternatives whenever possible will undoubtedly yield positive results both economically and sociologically speaking.
The collective efforts of individuals, communities and businesses will all play a significant role in addressing global warming and defending humanity from the long-term effects of climate change.
How can the world make a transition to a more sustainable future given the challenges presented by climate change?
Sustainability is the ability not only to meet current needs but also to ensure that future generations can meet their needs. Climate change is presenting new challenges. We need to take immediate action to end our dependence on finite resources.
To move towards a more sustainable future, it is important for us to reconsider our current models of consumption and production, as well as our dependence on natural resources such as fossil fuels. We need to find new technologies, renewable energy sources, and systems that can reduce harmful emissions and still meet our daily needs.
Additionally, sustainability must be approached from a holistic perspective. This means that all aspects are considered, including the materials used, waste management strategies and reuse strategies, as well energy usage in transportation and industry. There are many options available, including the use of renewable energies like solar, wind and hydropower, improved waste management systems, increased efficiency in agriculture, improved transport networks, green building regulations, and sustainable urban planning.
This goal requires behavioral changes from individuals in all sectors of society. Education programs are essential to assist people in understanding the impacts of climate change. They can also help them understand how they can contribute positively to a more sustainable planet through micro-actions like reducing food waste and adopting low-carbon lifestyles.
In the end, it is only through collaboration between industry leaders and citizens that we can make significant progress in creating more sustainable worlds for future generations.
How does climate change politics impact global efforts?
Climate change is a controversial issue that has caused a lot of division between nations, governments and individuals. The political positions of various actors have an effect on the implementation and effectiveness of measures to combat climate change. It is becoming difficult to reach consensus on global efforts for addressing this urgent environmental crisis.
A majority of scientists agree that climate change caused by humans is real and must be addressed immediately. The politics surrounding these issues often undermines global cooperation which is needed to make effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices, upholding regulations protecting natural habitats, researching viable technological solutions, and other climate change interventions.
Many governments around the globe want to protect business interests and enforce policies that restrict business activities. This often clashes with regulations that experts recommend for effectively addressing climate change. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
Differences in power dynamics among countries further complicate gaining full consensus on how best to tackle climate change. Countries with more economic power often appoint their own representatives to represent them on international bodies responsible for negotiations over the environment - this can lead to lopsided discussions of those countries' perceived interests versus the collective interest of all involved parties. The potential side effects of radical change like geoengineering, have been extensively discussed at both the national level and internationally.
At a grassroots level too, grassroots movements have struggled against powerful opponents including corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbies trying to maintain politically favorable positions for their industries especially when it comes to funding research into alternative forms of energy production or enforcing renewable energy technology mandates such as low emissions targets for vehicles etcetera - meaning individual governments must remain clearheaded about potential rewards and outcomes if they are going actively try to make valid progress on the matter in the question itself instead seeking public favor through short-term gains or even spectacles.
To mitigate the current environmental crisis, it will be crucial that resources are properly distributed and political divisions between countries are not overlooked.
What is the potential impact of land-use change and deforestation upon climate change?
Deforestation and land use change have a direct and immediate impact on the climate. Trees that are cut down or burnt can no longer absorb carbon dioxide. This is one of the most important greenhouse gasses on Earth. Therefore, when trees are cleared by deforestation or burned for agricultural purposes, less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere.
At the same time, changes in land use can also release more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. In addition to methane and nitrous oxide, pesticide and fertilizer use can increase when forests are converted into agricultural lands. Also, clearing can increase soils containing large amounts of carbon; these soils may be exposed to farming activities that turn them over or disturb them, which will release more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Deforestation, land-use change and other environmental impacts can cause more greenhouse gas emissions than they do. It can also affect regional air quality. As an example, deforestation smoke has been shown to reduce visibility and cause respiratory illnesses such asthma and other conditions. The global climate can change as a result of changes in local air quality. This is because more sunlight reaches the Earth's surface than the atmosphere.
In conclusion, deforestation and land-use change have resulted in a significant contribution to increased levels of global greenhouse gas emissions and have had negative impacts on local air quality that further contribute to climate change. Reducing these practices should be a high priority if serious efforts toward mitigating climate change are to take place promptly.
What impact does climate change have on food security and agriculture?
Climate change and global warming have a direct impact on agriculture and food security. The changing climate can affect rainfall patterns, temperatures, soil moisture levels, and extreme weather. This can disrupt farming activities, reduce crop yields and lead to losses of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures can lead to the proliferation of pests or diseases that affect crops; it can also cause shifts in ranges suitable for agricultural production. This could lead to an increase in food prices and a higher incidence of hunger worldwide.
Rising sea levels pose a further threat. They could inundate valuable agricultural land in many coastal areas, leading to higher salinity levels in wetlands, where important crops are grown. Livestock production is similarly affected by the changing climate - high temperatures during summer months can reduce fertility rates for animals like cattle, sheep, and goats, resulting in lower milk yields which exacerbate food insecurity across communities.
Global warming and climate change have a complicated relationship. However, adaptation strategies are being implemented by governments globally through strategic investments made in climate-smart farming (CSA). This means promoting sustainable methods, such as crop rotation and the preservation of native seed varieties. These strategies help prevent adverse effects from climate change or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
It is essential that farmers worldwide adopt technologies that are more responsive to changes in the environment when selecting the right crops to grow on specific parcels of land to ensure food security amid a rapidly changing environment. There must be improvements made to existing infrastructure in order to take the appropriate actions when critical crop thresholds fall. This includes installing stable irrigation networks that provide adequate access water at times when it is difficult for farmers to grow crops. For sustainable solutions to be created that will ensure the continued compliance with international dietary guidelines in our ever-changing climates, it is necessary to have a cohesive collaboration among all stakeholders. This includes government officials at international levels as well as NGOs located at local communities.
What is the impact of climate change on oceans and marine life around the world?
What is the impact of climate change on the world's oceans and marine life?
Since its inception climate change has significantly affected the world's oceans as well as the marine life associated with them. The depletion of the ozone layer, which causes constant oceanic warming, has caused major disruptions to marine ecosystems. This has led to coral bleaching and a decline in species.
Climate change may also be responsible for extreme sea level rises and more unpredictable weather conditions, which can prove to be fatal to coastal areas. Additionally, temperature changes may cause water systems to lose oxygen. This can result in "dead areas" in which abundant marine life is reduced.
Ocean acidification can also be caused by climate change. Excess carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere and accumulates in the oceans. Ocean acidification increases pH, which can disrupt the essential functions of animals that are unable to adapt, such as crabs, oysters, clams and crabs.
Higher temperatures can also change the location or shrinkage of natural habitats, making them less suitable for some species. This increase in ocean stress accelerates already high extinction rates amongst many species worldwide causing a severe imbalance between predators and prey that might eventually lead to complete extinctions.
The effects of climate change ripple throughout entire ecosystems influencing multiple species whether directly or indirectly through evaporation lowering water volumes or sharp temperature shifts jeopardizing any sustainable development for fisheries and other maritime activities. Global climate change continues to wipe out entire species of life on Earth, transforming our future lives not only on the land but also deep below the oceans' surface.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to make your home more efficient and fight climate change
You can make your home more efficient and reduce your carbon footprint. It will also save you money on your utility bills.
Make sure your home is well insulated and sealed. You must ensure that your windows and doors fit properly. If you find drafts around pipes or vents, make sure to add weather stripping and fill in any gaps with caulking around door frames and window frames.
Insulate your walls, ceilings, and floors to maximize energy efficiency. Inspect the attic for potential air leaks.
Lighting accounts for up to 18% of total household electricity usage so make sure you switch to LED light bulbs which use up to 80% less electricity than traditional incandescent ones! Installing motion sensors and timers will also help you save additional money by turning off lights as needed.
An old boiler or furnace can be replaced to save money on energy. They are also more efficient. A programmable thermostat allows you to control the temperature based on who is home and who is away.
All windows should be replaced by double-glazed units that are more energy efficient and less heat escaping. Low-flow showerheads, which are low in water consumption, can be bought. They maintain an adequate pressure level and reduce water usage.
ENERGY STAR rated appliances are more efficient than non-certified models and can use as much as 50% less power. It's important to remember the little things, such as not plugging your phone chargers or TV boxes, which could help you save significant amounts of energy.
These steps can make living at home easier and less stressful.