In order to fight climate change, it is important to understand how the government is addressing the issue. The United States is a leading nation, and the actions taken by the federal government can help to accelerate global action. However, there are a number of challenges to implementing this approach at home.
To combat climate change, the federal government has established policies that limit emissions from all parts of the economy. These include the Clean Air Act, which requires the Environmental Protection Agency to work with states to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Other laws require Department of Energy to set energy efficiency standards and work with private companies to develop clean technology.

Additionally, the Biden administration has adopted a "whole-of-government" approach to combating climate change, which includes a partnership with state and local governments. It is also working on reducing emissions from all major industries, including transport and electricity generation.
Many towns and cities across the country are also taking steps to reduce their carbon emissions. Some have already taken action to reduce their carbon footprint. Others are focusing on adaptation projects, such as developing heat-resistant pavements and improving water storage. Communities have the ability to plan for higher temperatures and help prevent disasters such floods.
Many countries around the globe are working together to fight climate change. South Korea and Japan have set new targets to lower their carbon emissions. While most countries are determined to achieve net-zero emission by 2050, some countries are increasing their ambition.
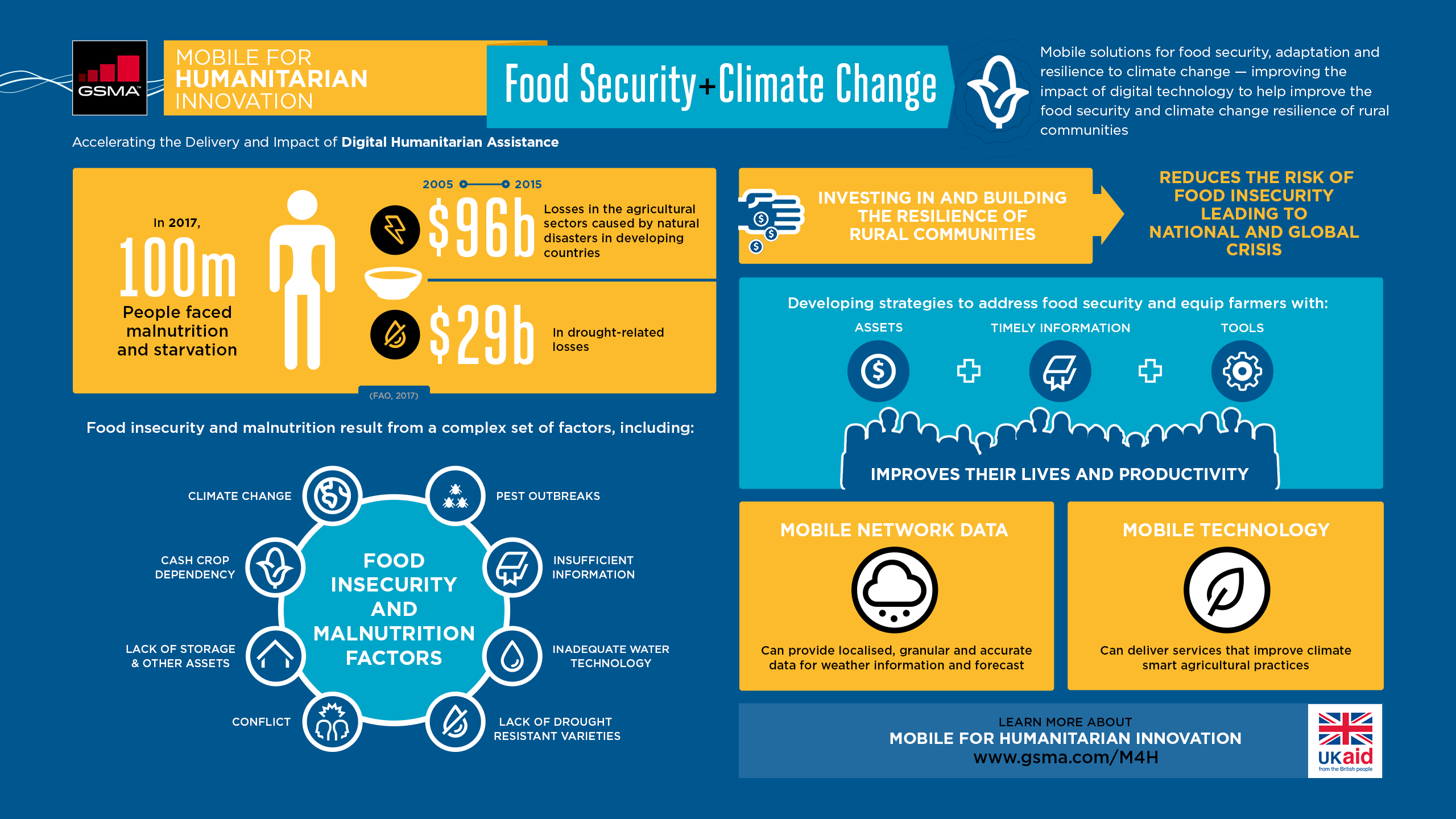
A large portion of the world's population is extremely vulnerable to the effects of climate change. People from the Pacific Islands are experiencing higher temperatures and sea-level rise. Indigenous Peoples are at the forefront of fighting against the fossil fuel industries. Many of these communities are also fighting against deforestation. It is a critical time to address climate changes, which are affecting every part of the world.

Climate change is a growing concern for the environment and public health. It is also a threat to the economy. In addition, it can lead to conflicts between nations over water supplies. The United States must act now if it wants to prevent global warming exceeding two degrees Celsius.
President Joe Biden is leading the effort to return the United States to its position of leadership in fighting climate change. The executive order, which was issued earlier in the year, required that the administration reduce its domestic greenhouse gases emissions by 50-52% by 2030 from 2005 levels. He encouraged Congress and the United States to tackle the climate crisis. Since taking office, President Biden has appointed former governors to his cabinet and enlisted the entire government in his effort.
The government is making progress, despite the difficulties in implementing policies at home. The Biden administration has made large investments in clean electricity and is determined to achieve half of its greenhouse gas reduction target by the end the decade. The administration has also embraced partnerships with the private sector as well the state, local and municipal governments.
FAQ
What are the current international efforts to combat climate change?
The current state of international efforts to address climate change is one of unprecedented unity and momentum. Countries from all over the globe are increasingly coming together to find ways to reduce their emissions, increase resilience against impacts and invest in renewable energy.
The Paris Agreement has been a catalyst for global action. Individual countries can set voluntary targets for reducing their carbon emissions by using the framework provided by the Paris Agreement. The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change and (UNFCCC) provides political guidance, as well as piloting initiatives such a carbon market.
In certain regions, there is progress as well. The European Green Deal, for instance, is a comprehensive set of legislation that aims to rebuild Europe's economy while African countries have committed to the African Renewable Energy Initiative. This Initiative aims to increase Africa’s global share of renewable energy production.
In addition to policy developments, action can be seen across sectors and industries; cities are actively transitioning toward sustainable public transport systems while society as a whole is embracing more sustainable lifestyles; companies are innovating technologies that drive down emissions while investors are reallocating their capital away from fossil fuels towards renewables.
Through the Common Reporting Framework (CFR), the 2021 Guidelines, the rich countries that are members of the OECD committee have agreed to common standards for reporting their national climate change actions.
All of these efforts show an unprecedented focus on climate action. Governments, civil society & private sector stakeholders alike must continue to build upon the momentum and push towards even greater ambition & progress if there is any hope of meeting Climate goals set by science & enshrined in international law.
What are the impact of deforestation and land use change on climate change?
Deforestation, land use change and other factors have an immediate and direct impact on climate. Trees that are cut down or burnt can no longer absorb carbon dioxide. This is one of the most important greenhouse gasses on Earth. Deforestation and burning of trees for agricultural purposes removes less carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Land use changes can also increase the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases. In addition to methane and nitrous oxide, pesticide and fertilizer use can increase when forests are converted into agricultural lands. Clearing can also increase soils with high levels of carbon stored in them; these soils can be disturbed or turned over by farming activities and release more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Deforestation, land-use change and other environmental impacts can cause more greenhouse gas emissions than they do. It can also affect regional air quality. The smoke from deforestation's burning events has been linked to poor visibility and other health concerns, such as asthma or other respiratory diseases. Because of the reduced amount of aerosol particles in our atmosphere, which scatter sunlight off the Earth's surface, these changes can have a cumulative impact on global climate.
The deforestation of land and the resulting changes in land-use have made a significant contribution towards increasing global greenhouse gas emission levels. These impacts have also had a negative impact on local air quality which has further contributed to climate change. These practices must be reduced if serious efforts are to reduce climate change.
Climate change: What is it and how can it happen?
Climate change refers the long-term shifts that occur in global weather patterns due to an increase in greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which causes global temperatures rise. This leads to many changes in weather and climate. This can include rising sea levels, melting glaciers, extreme storms and droughts, widespread coral reef bleaching, species extinction, and disruptions to food production.
Human activity is the major cause of climate change. These activities cause the atmosphere to heat up much faster than natural processes, like volcanic eruptions. They also emit many times more carbon dioxide than volcanoes.
Global greenhouse gas emissions are also influenced by deforestation, which contributes about 15-20%. The atmosphere is effected by the carbon dioxide stored in trees when they are cut down or burned. Additionally, forests act a natural carbon source that absorbs CO2 into the atmosphere. Without this capacity, carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere will continue to rise with devastating effects for ecosystems around world.
Human-caused pollution not only releases CO2, but also other harmful gases like methane (CH4) or nitrous oxides (N2O). While methane is used extensively in industrial processes, it contributes substantially to atmospheric heating. N2O comes primarily from soil management activities like fertilization and tilling that release excess nitrogen into the soil. This leads to N2O being produced upon microbial interaction.
The collective efforts of social, economic and political institutions must be made to drastically reduce the emissions and shift away from fossil fuel dependence. It could be possible to reduce atmospheric pollution by replacing polluting fossil fuels using smart solutions that encourage zero waste living. Reforestation projects, which are powerful aid in the fight against climate change by absorbing large quantities of CO2 back into nature and maintaining biodiversity, can help us take responsibility for our environmental impact.
How does the politics of climate change impact global efforts to address it?
Climate change has become a highly politicized topic that has caused great divisions among governments, nations, and individuals. Politicians of many actors influence the implementation of actions to address climate change. It is becoming difficult to reach consensus on global efforts for addressing this urgent environmental crisis.
The vast majority of scientific opinion agrees that human-generated climate change is real and requires urgent action. These issues are often dominated by politics, which can hinder global cooperation that is necessary to implement sustainable energy practices, protect natural habitats, research viable technological solutions, as well as other climate change interventions.
Most governments are eager to protect their business interests and enforce rules that will limit business activity as much as possible. This is often in conflict with the regulations experts recommend to combat climate change. Without strong commitments of all participating countries, and international action on a large scale, it becomes difficult for any state or group or states to effectively address climate-change legislation.
Further complicating the process of reaching full agreement on how to deal with climate change is the differences in power dynamics. The countries with greater economic power tend to nominate their own representatives to represent them in international bodies that are responsible for the environment. This can lead to biased discussions between the perceived interests of the country and the collective interest of all parties. The potential side effects of radical change like geoengineering, have been extensively discussed at both the national level and internationally.
In the same way, grassroots movements are fighting powerful opponents at the grassroots level. These include corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbyists looking to retain politically favorable positions.
To mitigate the current environmental crisis, it will be crucial that resources are properly distributed and political divisions between countries are not overlooked.
How does human activity affect climate change
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. In fact, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), humans are responsible for more than 70% of all global warming since the mid-20th century.
Burning Fossil Fuels: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This increases the already high levels of atmospheric CO2, which acts as a greenhouse gas by trapping heat from Earth's sun and increasing temperatures. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation - Trees which store atmospheric carbon dioxide within their trunks, when they absorb it through photosynthesis, are removed by deforestation. Also, cutting down forests can increase albedo - which is the amount reflected solar radiation going back into space. It also reduces solar heat absorbtion by the earth's surfaces and encourages excessive global warming. The deforestation of forests can also affect the local air quality, which is directly linked to respiratory problems.
Farming is responsible for 14% to 18% of all anthropogenic greenhouse emissions globally each year. Because of its high methane content, animal waste emits large amounts methane into the atmosphere. Reducing your intake of animal products is an effective way to lower your greenhouse gas emissions. Nitrous oxide can also be released into our atmosphere. This creates smog that harms our respiratory system.
Conclusion: While human activity has had a significant impact on the environment over centuries, technology advancements such as renewable energy sources have allowed us to look towards the future. The results of these industries, which emit carbon, will soon be clear when we use technology through green innovations to make it eco-friendly and reduce climate change. All people are safe in a healthy, prosperous natural world.
Statistics
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest in Clean Energy and Support the Transition to a Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy is a type of renewable power that doesn't produce any pollution or emit carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. It includes technologies such as solar photovoltaic, wind power, hydroelectricity, geothermal energy, and hydrogen fuel cells. Investing in clean energy sources can have many environmental benefits, such as reducing reliance on fossil fuels, reducing the amount of air pollution generated by traditional electricity methods, and providing more reliable electrical access to remote locations.
Investors have the opportunity to invest in clean-energy projects by purchasing shares of companies that create innovative technologies. This includes investing directly in stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) related to clean energy. Direct investments in start-ups and venture capital projects can be an option for investors to help fund research and development of clean energy technologies.
Clean energy investors support innovation that reduces harmful emissions from electricity generation. This investment can also help increase economic development through the creation of jobs in the production and engineering of renewable energy systems. Finally, putting money into clean energy can provide investors with a financial return due to tax incentives programs that are incentivizing investments into green technologies like wind farms, solar panels, and biomass heat generation systems.
We can help the transition to low-carbon by investing in companies that create electricity from renewable resources.